X-ray views
Using x-ray allows for 2D visualisation of a 3D structure.
A combination of different x-ray angles must be utilised to appreciate the structures in a 3D way.
Lesions in a coronary vessel which may be clearly visible in some x-ray veiws may be obscured or not clearly appreciated in alternate views.

Anterior - posterior (AP)
AP projection allows for visualisation of how the heart sits in the chest from directly face on.
The reverse PA, is not utilised during coronary angiograms. This would be if we were assessing the arteries by viewing the patient directly from behind
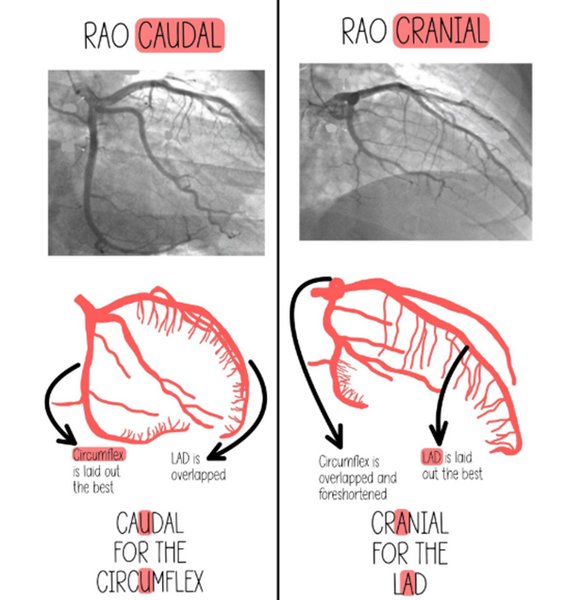
Right & left anterior oblique (RAO & LAO)
RAO projections allows for visualisation of how the heart sits in a side on fashion, with the atria positioned towards the left of the screen, the ventricles towards the right of the screen, superior and anterior views at the top of the screen and inferior views at the bottom of the screen.
LAO projections allows for visualisation of how the heart sits as if facing down the tricuspid and mitral valves, with the septum in the middle, the right on the left side of the screen, the left on the right hand side of the screen, the inferior at the bottom middle of the screen and anterior at the front top of the screen.

Caudal & Cranial
Cranial projections allows for top-down visualisation of the heart whereas caudal projections allow for bottom-up visualisation. Cranial views are often utilised to help visualise the LAD and diagonal branches whereas caudal views help visualise the LCx and the LMCA.