Assessing CA lesion significance
X-ray assessment
-
Minimal 1-24%
-
Mild 25-49%
-
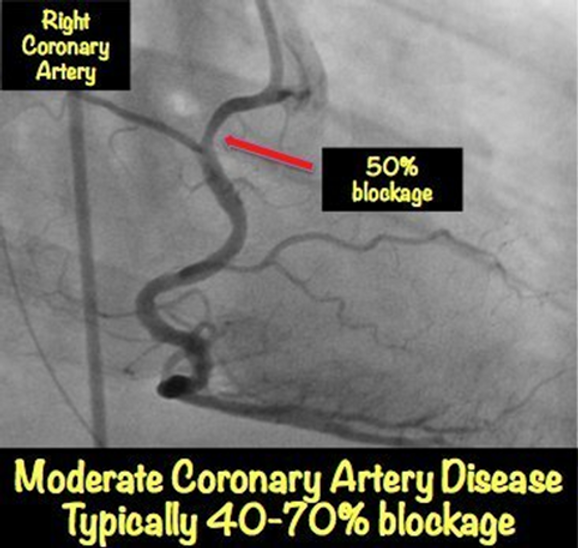
Moderate 50-69%
-
Severe 70-99%
-
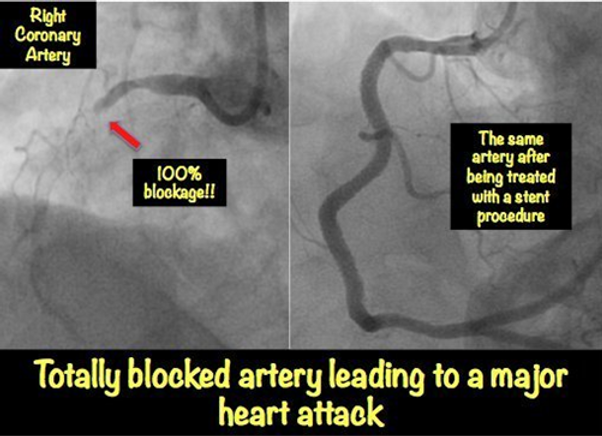
Complete Occlusion 100%
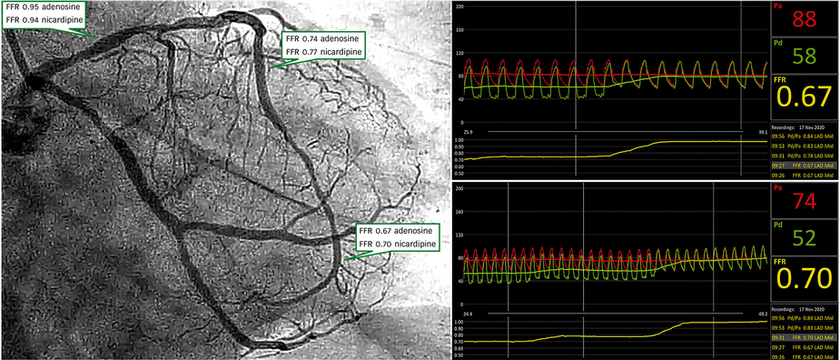
Fractional flow reserve - FFR
Measures the pressure difference during hyperemia (maximum blood flow) by comparing the difference as a fraction.
Hyperemia is achieved by administration of Adenosine (infusion).
Results:
0.8-1.0 Normal
.75-.8 Borderline
<.75 Significant lesion

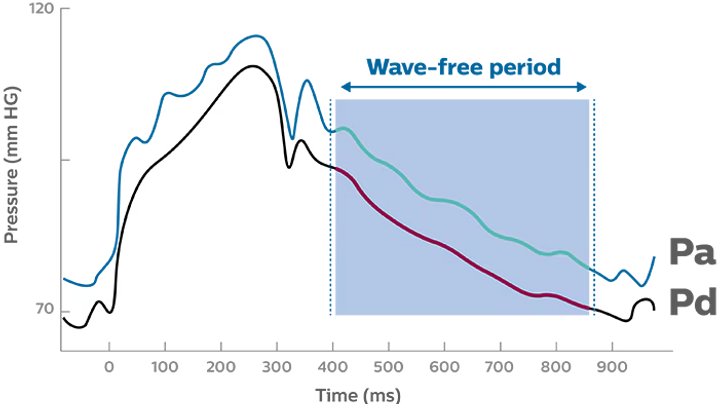
Instant wave free ratio (IFR)
Assesses a resting difference (no need for Adenosine) in pressure as a ratio.
The pressure is measured in the wave free period in diastole, where the microvascular resistance is stable and a linear relationship exists between distal pressure and flow velocity
Results
>0.90-1.00 Normal
<.90 Significant lesion
Resting full-cycle ratio (RFR)
Assesses pressure difference as a ratio, similar to FFR, except is measured during a resting difference (no need for Adenosine) .
Results
>0.90-1.00 Normal
<.90 Significant lesion

Index of microvasculature resistance (IMR)
Measures the resistance of the micro vessels using a pressure temperature guidewire.
It can be used to assess
-
severity of microvascular disease (INOCA (Ischemia with No Obstructive Coronary Arteries))
-
can help predict/assess infarct size
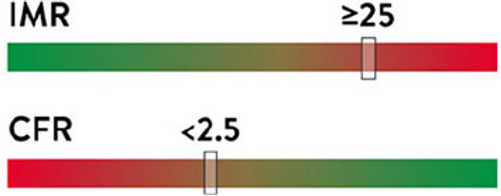
Results
<26 normal
>25 abnormal
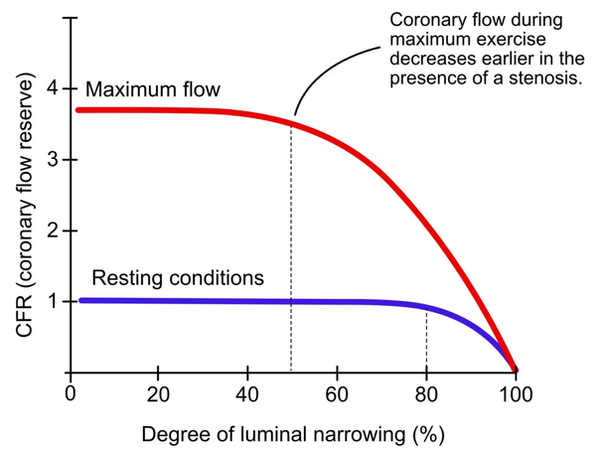
Coronary Flow Reserve (CFR)
Another way of assessing severity of microvascular disease
Measures the change in blood flow from baseline compared to when hyperemia is induced.
Results
3-5 normal
<2 abnormal
Intravascular ultrasound (IVUS)
IVUS involves a cross-sectional view of the artery, highlighting where the normal artery wall ends and the plaque begins.
The different layers of the artery can be appreciated in the IVUS.
Can be used to estimate the severity of a lesion and can in aid in appropriate stent and balloon sizes.
Dissection, stent underdeployment, and thrombosis can also be appreciated with IVUS.
Artery layers
-
Adventitia
the outer covering of the artery
-
Media
the wall of the artery
-
Intima
a layer of endothelial and other cells that make direct contact with the blood inside the artery
normal arteries: thin layer
diseased arteries: thickened by plaques or other tissue growth, which are often eccentric or asymmetrical
-
Lumen
the open channel of the artery where the blood flows through


Optical coherence tomography (OCT)
Provides high resolution imaging of the coronary arteries
Can help differentiate plaque and clots, assess vessel size and assess stent malapostion





