Atrial fibrillation (AF)

AF basics
Purpose
AF ablation is performed as a rhythm control strategy.
AF ablations can be performed endocardially or as a surgical ablation
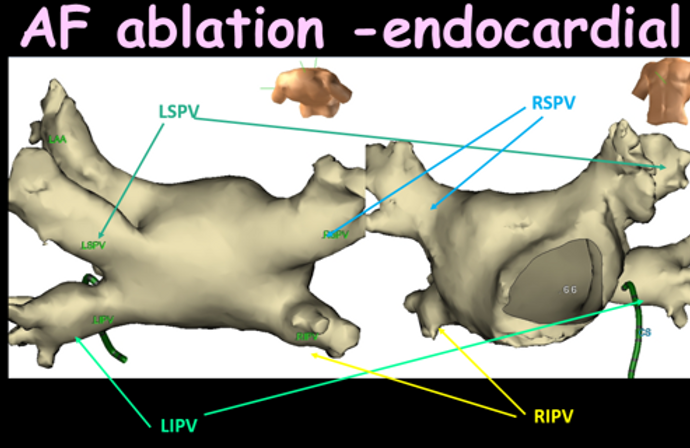
Endocardial pulmonary vein isolation (PVI) is performed for paroxysmal AF using ablation technology.
Back wall isolation may be used for persistent AF.
Success rate
Varies from 55-80%
Dependent on persistence (ablation for PAF more successful than persistent)
Long term success rates increase with multiple procedures
Complications
As AF ablations involve transeptal puncture, complication rates are higher compared to right sided EP studies.
Complications may include
-
tamponade /perforation
-
stroke
-
hematoma
Overall complication risks quoted to vary between 2.5-4.5%
AF ablation
Equipment
-
Venous access multiple sites
-
Often a decapolar coronary sinus catheter is used (not always)
-
Transeptal equipment (sheath and needle - multiple (2) punctures may be performed - Dr dependent)
-
Ablation catheter
-
+ / - 3D mapping catheter
Procedure
-
Venous access obtained
-
Coronary sinus catheter positioned
-
Transeptal puncture performed
-
If 3D mapping is used, 3D geometry of the left atrium will be collected
-
Ablation of the PVs + / - back wall will be performed
-
Other AF triggers may be targeted (e.g., SVC)
-
Entrance and exit block is confirmed.
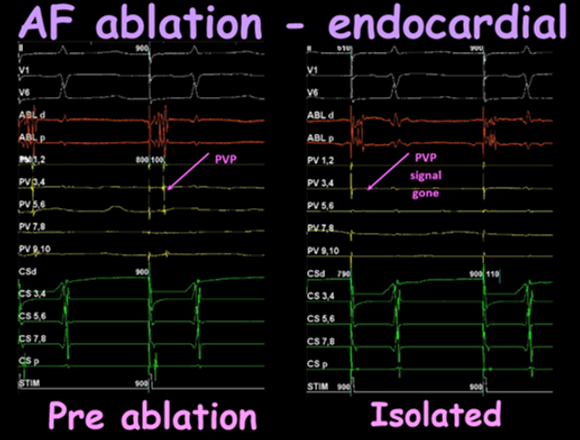
This image demonstrates pacing the atrium from the distal coronary sinus. Pre ablation the left atrium conducts into the pulmonary vein (pulmonary vein potential (PVP)). Once isolated, the PVP is gone demonstrating electrical isolation in the pulmonary vein.
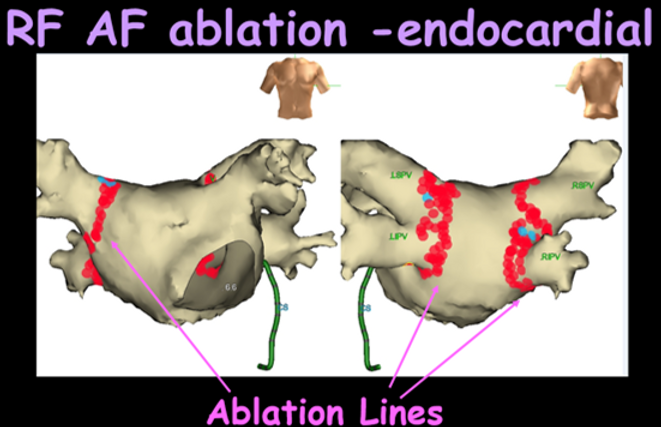
Radiofrequency (RF) ablation
Veins are isolated by application of RFA using point to point ablation.
A 3D map is required to perform RFA
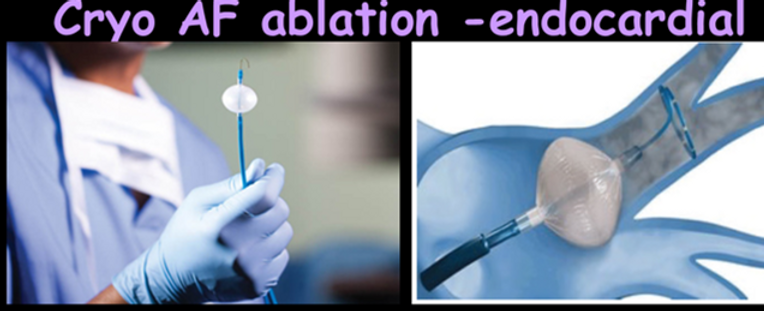
Cryothermy ablation
Only veins can be targeted with cryothermy ablation.
The balloon catheter is inflated at the ostium of the PV where cryothermy is performed.
Pulsed field ablation (PFA)
Current availabilities of PFA catheters for AF are similar to cryothermy ablation catheters in terms of shape.


The above picture is of the Boston Scientifics Farapulse PFA catheter.
The flower pose (top) is used to ablate the antrium of the pulmonary veins, whilst the basket pose (bottom) is usd to ablate the ostirum of the pulmonary veins.
The backwall is isolated in flower pose.

The above picture is of the Medtronic pulse select PFA catheter.
Both veins and backwall can be targeted with this catheter

The above picture is of the Medtronic Sphere 9 PFA catheter.
The above picture is of the Abbott Volt catheter.






