Pacing in tachycardia
HIS synchronous VPB / Zipes
What is ZIpes?
-
Zipes involves adding a paced VPB during tachycardia when the HIS is refractory.
-
This means that it is impossible for the VPB to have retrograde conduction up the AV node due to refractoriness.
-
If there is any change is the following A-A interval this demonstrated an extra circuit is present in the heart (accessory pathway)


How to perform
-
Sensed extra with Ventricular stimulus faster rate than TCL
-
Cease when tachy terminates or V appears to be HIS synchronous
Confirming beat is HIS synchronous
-
Ensure ventricular capture
-
Measure H-H interval on beat prior to paced beat
-
Drag caliper onset to His – prior to stimulus and lock in
-
Measure how early pacing artefact is compared to caliper offset
-
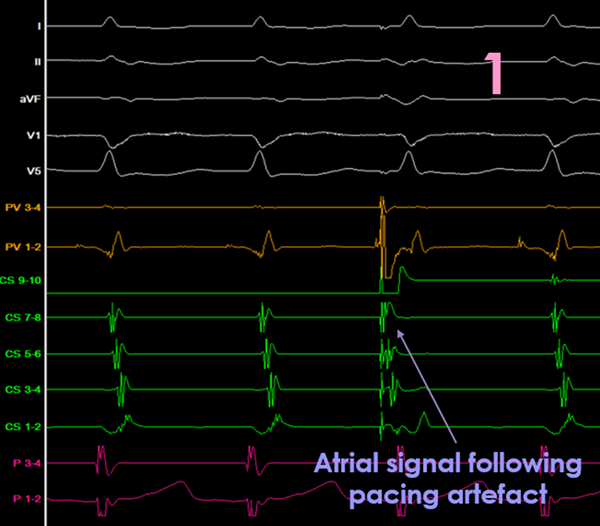
See if there is any effect in timing for the following atrial event




Responses to Zipes
No change in A-A
-
consistent with AVNRT
-
AVRT is not ruled out
Tachycardia termination with no A
-
active AVRT pathway
Delay in A-A interval
-
active decremental AVRT pathway
A-A advancement
-
could be an active pathway or
-
a bystander pathway
*ventricular advancement/delay proves active pathway
Ventricular entrainment

How to perform
-
Paced 20-30ms faster than TCL in the ventricle until ~10 capture beats
-Pacing for too long or too fast may terminate tachycardia
-Pacing too slow will not capture the ventricle
Confirming entrainment
-
Ensure there is ventricular capture
-
Ensure the same tachycardia continues when coming off pacing
-
Measure A-A interval on the last few beats to ensure A is entrained
-
View response immediately after
-
Measure the 1st return atrial event to ensure there is no pseudo VAAV response
-
Measure PPI-TCL by measuring stimulus artefact to return signal on paced catheter
-
Measure Stim-A – VA by measuring stimulus-entrained A & compare to tachycardia VA
-
Look at the start of the entrainment and choose the 1st fully capture ventricular event
-
Measure forward the A-A intervals until you see a AA interval that equals the ventricular entrainment rate







Responses to Entrainment
Immediate response
-
VAV: nodal involvement (AVRT/AVNRT)
-
VAAV: atrial tachycardia (ensure is not pseudo VAAV)
Post pacing interval - tachcardia cylce length (PPI-TCL)
-
>115ms AVNRT
-
<115ms septal pathway
Stim A interval - VA interval
-
>85ms AVNRT
-
<85ms AVRT
Number of beats to entrain the atrium
-
1 AVRT
-
>1 AVNRT



Late & Early APBs
How to perform
-
Sensed extra with Atrial stimulus faster rate than TCL
-
Cease when tachy terminates, A appears to be HIS synchronous or risk of AF
Confirming late APBs
-
Confirm there is atrial capture
-
Measure H-H / V-V interval on beat prior to paced beat
-
Ensure the immediate beat is not effected
-
Measure the following H-H / V-V to see if there is any change in interval compared to the TCL
-
If there is a change in VV, measure the VA interval and compare to Tc VA




Confirming early APBs
-
Confirm there is atrial capture
-
Measure H-H interval on beat prior to paced beat
-
Ensure the immediate beat is effected
-
Observe the response after
-
If tach continues, compare immediate VA to Tc VA




Responses to APBs
Late APB
-
HV advanced
-consistent with AVNRT (if unchanged VA)
-consistent with atrial tachycardia (if VA is unlinked)
-could still be junctional tc if slow pathway is present (not rules out)
-
HV delayed
-consistent with AVNRT (linked VA)
consistent with atrial tachycardia (unlinked VA)
-
Tachycardia terminated
-consistent with AVNRT
-
No change
-consistent with junctional tachycardia
Early APB
-
Tachycardia continues
-consistent with junctional tachycardia
-consistent with atrial tachycardia (if VA is not linked)
-
Tachycardia terminates
-consistent with AVNRT
(fast pathway interrupted for short VA tc, slow pathway interrupted for long VA tc)
Atrial entrainment
How to perform
-
Paced 20-30ms faster than TCL in the atrium until ~10 capture beats
-Pacing for too long or too fast may terminate tachycardia
-Pacing too slow will not capture the atrium
Confirming entrainment
-
Ensure there is atrial capture
-
Ensure the same tachycardia continues when coming off pacing
-
Measure V-V interval on the last few beats to ensure V is entrained
-
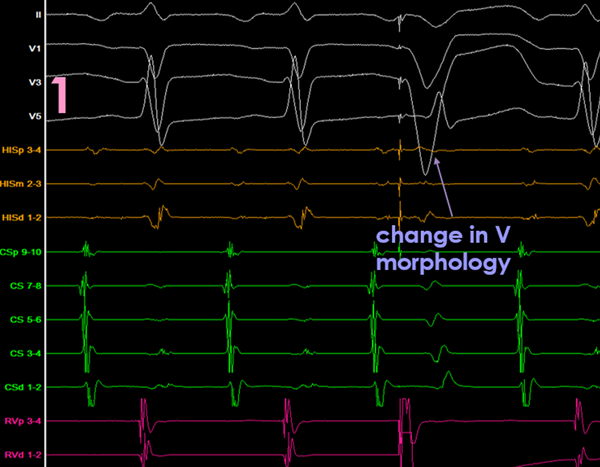
View the morphology of the entrained V beats
-
View response immediately after





Responses to atrial entrainment
SVT
-
AVA response
-
No change in ventricular morphology
VT
-
AVVA
-
change in ventricular morphology




