Triple threat
-rhythm shifts & diagnostic rifts-
Patient presentation
-
21 year old male
-
recurrent palpitations
-
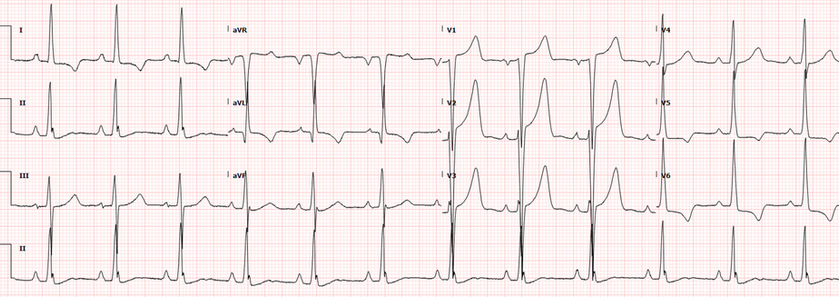
documented tachycardia on ECG
-broad complex, regular tachycardia

Differential diagnosis
-
SVT with aberrancy
-
Ventricular tachycardia
-
Antidromic AVRT
Baseline ECG/EGM
-
AH: 82
-
HV: -12


Retrograde incremental pacing
-
Midline, decremental retrograde atrial activation (earliest CS 9,10)

-
Change in atrial activation pattern at faster rates - eccentric (CS 1,2)

Atrial incremental pacing
-
Increase in pre-excitation with faster rates
-
Atrial latency noted
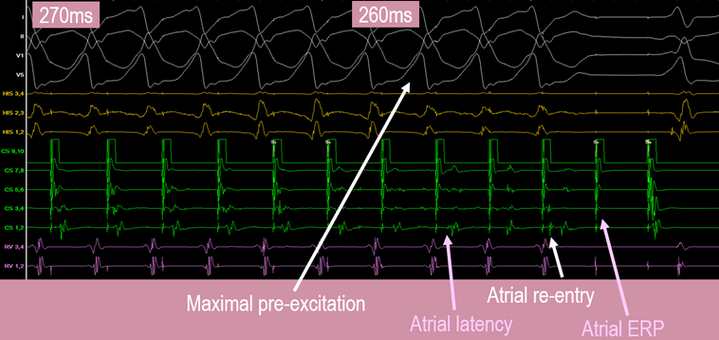
Antegrade paced extras
-
Increase in pre-excitation
-
Atrial latency on extra
Tachycardia 1 Induction
-
Ventricular paced extras
-
Some variation in 1st few atrial beats prior to tachycardia settling
TCL 300, VA 94
Eccentric VA conduction (CS 5,6 earliest)

Tachycardia 1: HSVPB
-
No change in A-A interval
-
Nothing ruled out

Tachycardia 1: Ventrainment - 330ms
-
Terminated arrhythmia - unable to observe post entrainment response
-
<1 beat to entain the atrium when venticle is fully captured.
-
Change in atrial activation pattern with entrainment (bystander pathway - pattern 3)
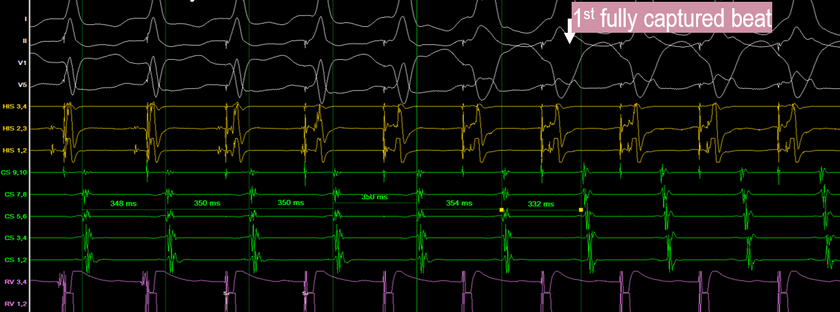
Tachycardia 1: V entrainment 2nd attempt- 270ms
-
VAHV response
-
PPI-TCL = 410-296 = 114 (borderline numbers- but not septal pathway)
Stim A - VA = 94 (borderline numbers- but not septal pathway)

Tachycardia 1 Diagnosis

Tachycardia 2: induction
-
Induced with atrial sensed doubles on Isuprel
TCL 280 VA 80
Eccentric VA conduction (CS 1,2)

Tachycardia 2: V entrainment 270ms
-
change in atrial activation pattern during entrainment
-likely bystander

Tachycardia 2: HSVPB
-
change in atrial activation pattern with atrial advancement
-tachycardia 1 bypass tract acting as bystander for tachycardia 2

Tachycardia 2: ablation
-
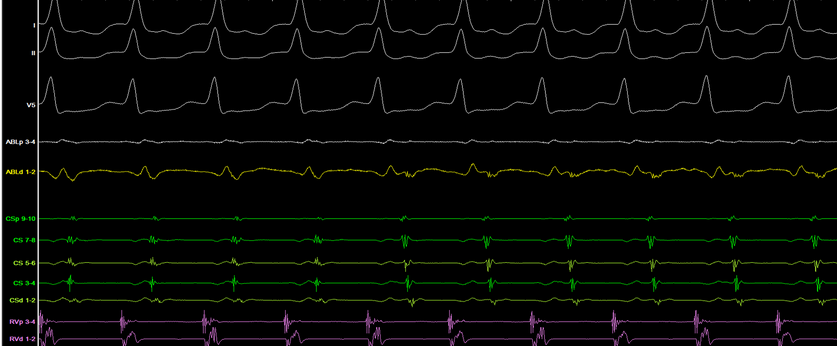
Mapped to postero-lateral LA


-
Change in atrial activation pattern during ablation to atrial pattern 3
(tachycardia 2 terminate)
Tachycardia 2: post ablation
-
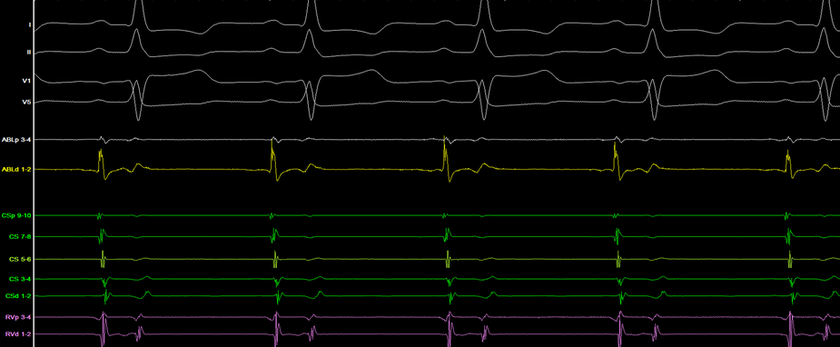
loss of pre-excitation
-
no inducible tachycardia 1 or 2
Tachycardia 3: ablation
-
CS 9,10 activation pattern earliest
(acted as bystander to previous tachycardia with entrainment on 1st beat - consistent with pathway) -
Mapped to antero-septal RA - ablated with cryo


Tachycardia 3: post ablation
-
VA conduction midline & decremental
VA wenckebach 600ms

-
No pre-excitations
-
AV nodal wenckebach 280ms

-
Atrial sensed extras
-echoes (mechanisms unclear)
-no inducible tachycardia (very easily inducible (each tachycardia) prior to ablaion)

Post op ECG
-
ST / T wave changes on ECG
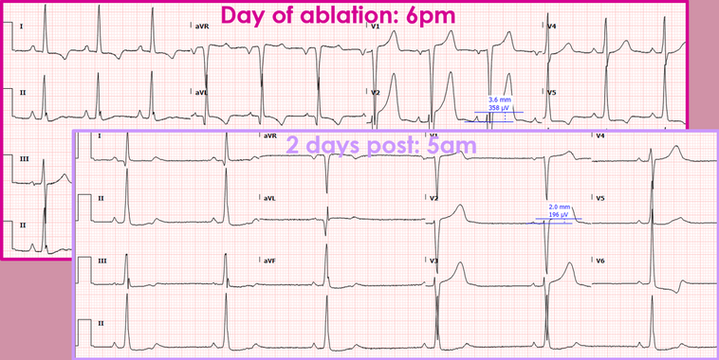
T wave memory
-
T wave abnormalities occur in patients with WPW due to abnormal ventricular activation and therefore repolarisation to the additional bypass tract(s).
-
After ablation of a bypass tract, the abnormal T wave may remain (memory), but tends to improve/disappear within weeks to months.
-
Persistent T wave changes are often mistaken as myocardial ischemia.
References
-
Helguera, M. E. et al., (1994). Memory T waves after radiofrequency catheter ablation of accessory atrioventricular connections in wolff-parkinson-white syndrome. Journal of Electrocardiology, 27(3), 243-249
-
Kanjwal, K. et al., (2021). What Is the Response Seen During Para-Hisian Pacing? Journal of innovations in cardiac rhythm management, 12(9), 4677-4680.





