Types of conduction block
Sinus pauses
Causes
-
high vagal tone
-
hypoxia
-
hyperkalemia
-
sleep apnea
-
medications (digitalis, beta blockers, etc)
-
sick sinus syndrome (can be degenrative, due to MI, myocarditis, etc)
Sinus arrest
failure of automaticity of the sinus node resulting in pauses

Sinoatrial exit block
block in the conduction of the electrical impulse from the sinus node resulting in a pause
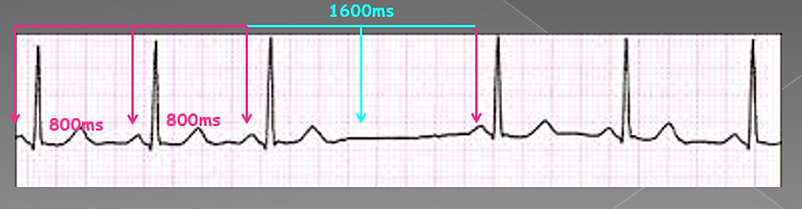
AV node block
Block at the level of the AV node.
May be supra or infra hisian.
1st degree AV block
When there is prolonged AV conduction
This will appear as a delayed/long PR interval (>200 ms)
Typically associated with high vagal tone (sleep, excessive pain, etc), acute MI (AV nodal ischemia), medication induced (beta blockers, amiodarone, calcium channel blockers), rheumatic fever, heart disease, electrolyte imbalance,

2nd degree AV block - type I
There is progressive PR lengthening followed by a non conducted P wave.
Also known as Wenckebach.
May result in a 2:1 AV pattern, which some may confuse for 2nd dgree AV block type II.
Typically associated with high vagal tone (sleep, excessive pain, etc), acute MI (AV nodal ischemia), medication induced (beta blockers, amiodarone, calcium channel blockers), rheumatic fever, heart disease, electrolyte imbalance

2nd degree AV block - type II
Advanced heart block which involves infra hisian block.
Often, but not exlusively presents with a broad complex.
Some sources will label a single dropped p wave as 2nd degree AV block. This is incorrect.
Typically associated with age, acute MI (AV nodal ischemia), heart disease, drug induced (beta blockers, amiodarone, calcium channel blockers), rheumatic fever, heart disease, electrolyte imbalance
Cannot prove unless an EP study is performed


Complete heart block/3rd degree AV block
Complete dissociation of atrial and ventricular activity. More P waves than QRS complexes.
Can have a narrow escape (nodal) with typical rates between 30-60 bpm or a broad ventricular escaoe typically slower than 40 bpm.
Typically associated with age, acute MI (AV nodal ischemia), heart disease, drug induced (beta blockers, amiodarone, calcium channel blockers), rheumatic fever, heart disease, electrolyte imbalance.
Narrow escape

Broad escape

High grade AV block
Not complete heart block (some AV conduction as normal), but has segments of complete heart block where several sinus beats may be non conducted (ventricular standstill/ventricular asystole).
Typically associated with diseased sinus node or AV node or dying heart.

Isorhythmic AV dissociation
Not true AV block (not CHB)
Occurs when ventricular (junctional) rate is > then sinus rate.
P waves and QRS appear at similar times but there is no relation between the 2
Often seen with high vagal tone

Bundle branch & fasicular blocks
WHen there is conduction block in one of the bundle branches or fasicles.
Often seen secondary to MI, and with congenital heart disease or cardiomyopathy
Right bundle branch block (RBBB)
Activation of the RV is delayed as depolarisation occurs via the septum from the LV
QRS is broadened (>120 ms)
RSR pattern in V1
May see ST depression/T wave inversion in V1-V3


Left bundle branch block (LBBB)
Activation of the LV is delayed as depolarisation occurs via the septum from the RV
QRS is broadened (>120 ms)
Deep S wave (largely –ve) in V1
T wave discordance – ST segments & Twaves in opposite direction to QRS complex
Poor R wave progression in chest leads


Left anterior fascicular block (LAFB)
Activation of the LV occurs via the posterior fascicle only which inserts into the
infero-septal wall of the LV
QRS is normal or slightly prolonged
Deep S wave (largely –ve) in inferior leads (II, III, aVF)
Results in left axis deviation


Left posterior fascicular block (LPFB)
Activation of the LV occurs via the anterior fascicle only which inserts into the upper, lateral wall of the LV
QRS duration is normal or slightly prolonged
Deep S wave (largely –ve) in V1
Results in right axis deviation






