Other
Dextrocardia
A condiA condition where the heart lies in the right hemithorac and its apex points to the right.
Features
-
Right axis deviation
-
+ve QRS, P and T waves in aVR
-
-ve QRS, P and T waves in I
-
Absent R wave progression in chest leads (dominant S waves throughout

Wolf-Parkinson-White syndrome
Occurs when electrical impulses travel from the atria to the ventricles through an accessory pathway, causing the ventricles to depolarise earlier than they normally would (via AV nodal conduction).
Known as “pre-excitation” on ECG
PR interval is short (<120 ms)
QRS is broad (>120ms) with an initial slurring upstroke on the QRS
May be associated with repolarisation changes
May have higher risk of SCD depending on pathway properties

Brugada
Congenital genetic disorder of sodium channel SCN5A
Coved ST elevation in V1-V3 >2mm
Partial/incomplete RBBB
Associated with SCD (VF + TdP)
More often seen in south-eastern Asia


Pericarditis
Involves inflammation of the pericardium
May result in chest pain, dyspnoea, tachycardia, fever, weakness, chills
Widespread concave ST elevation on ECG (due to epicardium involvement)
Widespread PR depression
Often seen with sinus tachycardia

Acute pulmonary embolism
Pulmonary embolism (PE) occurs when a blood clot or other foreign matter lodges in a pulmonary artery causing obstruction of blood flow to lung.
Symptoms: severe dyspnoea, chest pain, nausea, dizziness, neurological side effects (anxiety, confusion etc).
ECG
-
sinus tachycardia
-
S1Q3T3 pattern
-
May result in RBBB
-
May have right axis
-
May have T wave inversion 1-3

Chamber enlargements
Enlargment of the atria or ventricles often occurs when heart disease forces them to accomodate greater pressure/volume
RA enlargement
Results in a peaked P wave (P pulmonale)
>2.5mm in inferior leads (II, III and aVF)
>1.5mm in V1 and V2
Principle cause pulmonary HTN
Chronic lung disease
Tricuspid stenosis

LA enlargement
Results in a notched P wave (P mitrale)
Classically seen with mitral stenosis
Lead II
-
Bifid P wave with >40ms between 2 peaks
-
Total P wave duration >110ms
V1
-
Biphasic p wave with –ve portion >40ms
-
Biphasic p wave with –ve portion >1mm
Sometimes seen with LVH & associated with
-
Systemic HTN
-
HCM
-
AS
-
LVH
-
mitral stenosis

RV enlargement
Voltage criteria
-
R wave
-
II, III >7mm
-
V1 >7mm
Other features
-
Right axis deviation
-
Downsloping ST segments of 1mm or more in leads II, III, aVF and V1 (sometimes also in V2-V3)
-
T wave inversion in leads II, III, aVF and V1 (sometimes also in V2-V3)
Associated with
-
pulmonary valve stenosis
-
congenital defects (septal defects)
-
pulmonary hypertension
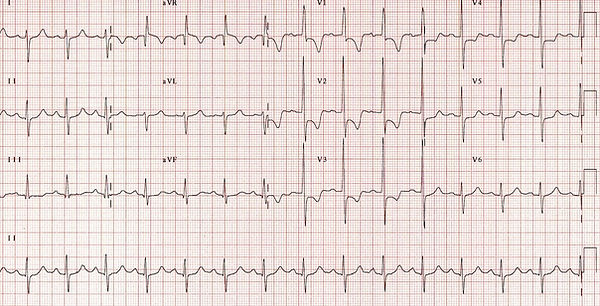
LV enlargement
Voltage criteria
-
S wave
-
III >20mm
-
V1/V2 >30mm
Other features
-
Downsloping ST segments of 1mm or more in leads I, aVL and V5-V6
-
High ST take off appearance in V1-V3
-
T wave inversion in leads I, aVL and V5-V6
-
May have left axis deviation
Associated with
-
AS
-
hypertension
-
HCM





