Intro to ECG
What is an ECG
ECG stands for electrocardiograph
An ECG is performed to determine a patients' heart rate and rhythm and identify if there are any conduction abnormalities.
Patient Identification
It is very important to confirm the patient details match the patient in front of you.
3 Steps to correct identify
Patient must state all of the following
-
Full name
-
Date of birth
-
Address
Conduction system of the heart

Features on an ECG

Hooking up an ECG
Components
-
ECG electrodes
-
ECG machine
-
Leads/Cables
Limb leads (4)
Chest/Precordial leads (6)
Chest Leads
6 unipolar leads
-
V1: 4th intercostal space, right sternal border
-
V2: 4th intercostal space, left sternal border
-
V3: between V2 and V3
-
V4: 5th intercostal space, left mid-clavicular line
-
V5: 5th intercostal space, left anterior axillary line
-
V6: 5th intercostal space, left mid axillary line

Limb leads
4 leads
-
Right leg (RL): inside calf, midway between knee & ankle on the right
-
Left Leg (LL): inside calf, midway between knee & ankle on the left
-
Right arm (RA): inside arm, between elbows and wrist on the right
-
Left arm (LA): inside arm, between elbows and wrist on the left
4 limb leads produce
-
3 unipolar leads – (aVF, aVL, aVR)
-
3 bipolar leads – (I, II, III)

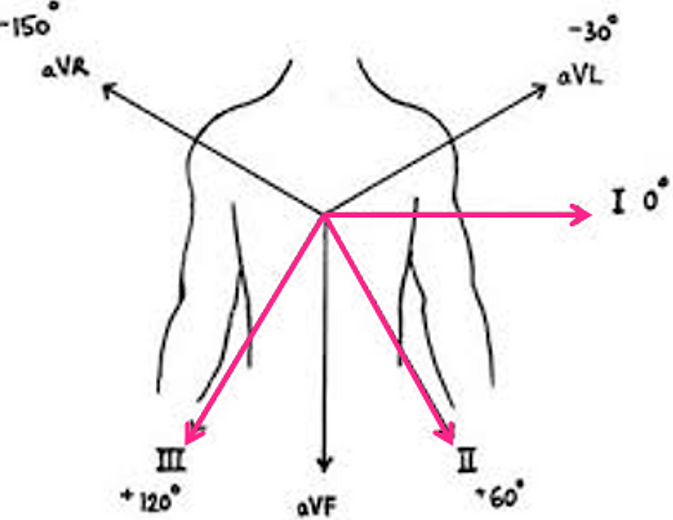
12 lead ECG views
Septal: V1-V2
Anterior: V3-V4
Lateral: V5-V6
Inferior: II, III, aVF
High lateral: I and aVL

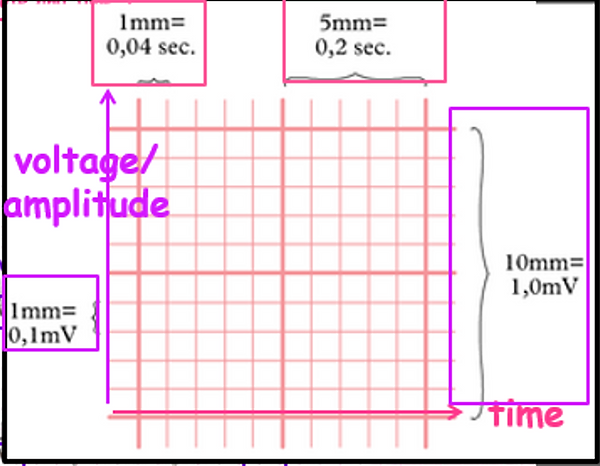
Information on an ECG

Correct ECG positioning - limb leads

Limb lead reversal

Reverse right arm and leg
Correct ECG positioning - chest leads

Identifying artifact on ECG
Important to get a clean quality ECG
Avoid external interference which may mimic or obscure true physiological recordings.
Common forms of artifact include
-
Muscle artifact
-
Movement artifact
-
Electrical interference – 50 Hz
-
Wandering baseline
Clean recording

Muscle artifact
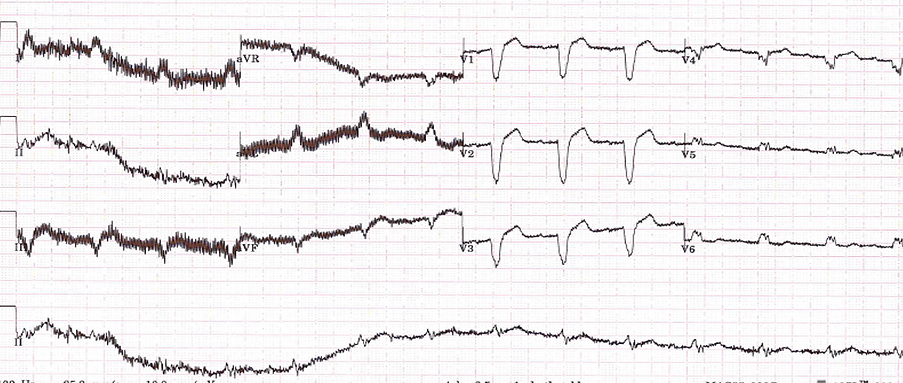
Muscle artifact

Movement artifact

Electrical interference

Electrical interference

Wandering baseline





