Repolarisation abnormalities
STEMIs
ST elevation changes occur in acute MIs, and are usually seen minutes after the onset of infarction.
The ST elevation occurs in the leads in the zone of the infarction (e.g., inferior leads (II, III, aVF) for inferior infarctions).
ST segment is considered elevated if >1mm above isoelectric line.
ST elevation requires urgent medical attention.
Anterior STEMI -ST elevation predominantly in V2-V5
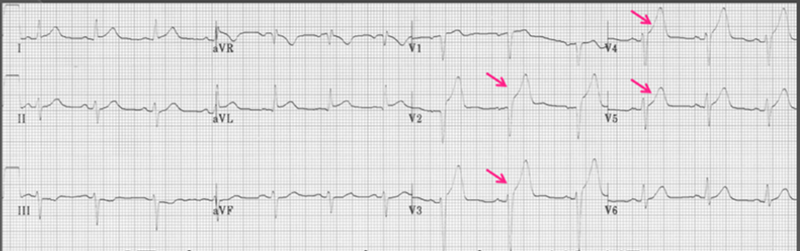

Inferior STEMI -ST elevation predominantly in II, III and aVF
Myocardial ischemia
Myocardial ischemia can result in ST depression and T wave inversion
These changes occur in the leads in the zone of the affected area
ST depression can be upsloping (A), downsloping (B) or horizontal (C). (upsloping is non-specific)
T wave inversion is at least 1mm deep and present in >2 continuous leads that have dominant R waves (R/S ratio >1)
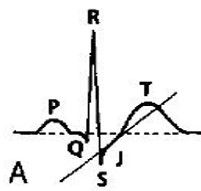
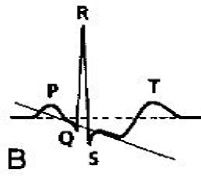
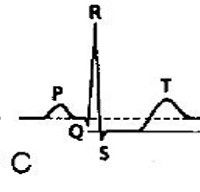
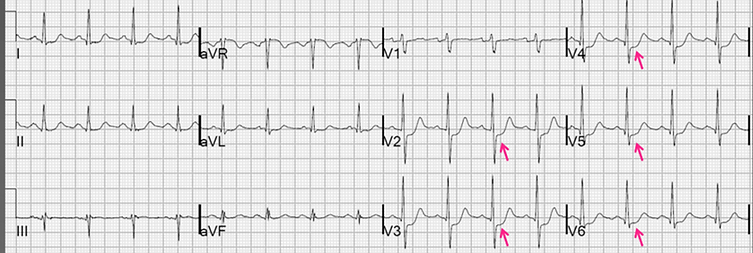
Horizontal ST depression predominantly in V2-V6 (anterior region)

T wave inversion predominantly in lateral leads V5, V6, I and aVL
Early repolarisation
ECG pattern commonly seen in young healthy patients.
ST elevation ~1-3mm or more in leads I, II and aVF and V2-V6
ST segments are concave
The J point is elevated before the ST segment
Significance unknown (? correlation with SCD)
Has been classified as benign


Long QT
When QT interval is long (m/f: >450/460)
Associated with SCD
Marked vulnerability to VF/Torsades de Pointes

Short QT

When QT interval is short (m/f: >350/360)
Associated with SCD
Marked vulnerability to VF/Torsades de Pointes




