Device algorithms to minimise AF
Abbott
•AF suppression
•Atrial protection interval
Biotronik
•Overdrive pacing
•Atrial upper rate
•Atrial ATP (aATP)
Boston Scientific
•Atrial preference pacing (APP)
•Atrial flutter response
Medtronic
•Post mode switch overdrive pacing (PMOP)
•Atrial preference pacing (APP)
•Non competitive atrial pacing (NCAP)
•Reactive (Atrial) ATP
Microport/Sorin
•Overdrive
•Pause suppression
•PAC acceleration
Abbott
AF Suppression
•To stimulate the atrium at rates faster than the intrinsic atrial rate in order to overdrive and suppress paroxysmal or persistent AF.
•The device continually searches for two P-waves within a 16-cycle window. Upon detection, the device pulses the atrium at a rate of increase that is determined by the current paced rate and Lower Rate Overdrive and Upper Rate Overdrive settings.
•The overdrive pacing continues for a programmable number of pacing cycles then steps down at a rate determined by the Rate Recovery (non-programmable) and returns the device to operation at the Base Rate, Rest Rate, or sensor-indicated rate. Upon continued detection of intrinsic atrial beats, the algorithm will again overdrive the sensed conduction.

AF suppression - programming
No. overdrive pacing cycle
•The number of cycles the device will overdrive the stimulation rate before decreasing the rate to the programmed Base Rate, Rest Rate, or sensor-indicated rate. Once the programmed number of cycles have been completed, the device begins to lower the stimulation rate based on the Rate Recovery parameter.
Lower rate overdrive (set at 10 min-1)
•is the amount of increase in the atrial rate added to stimulation rates below 59 min-1. Thus, if the current AF Suppression rate = 55 min-1, then AF Suppression would add 10 min-1 to the stimulation rate to pace the atrium at 65 min-1.
Upper rate overdrive (set at 5 min-1)
•is the amount of increase added to stimulation rates above 151 min-1. Thus, if the current AF Suppression rate = 155 min-1, then AF Suppression would add 5 min-1 to the stimulation rate to pace the atrium at 160 min-1.


Atrial protection interval
Atrial protection interval (API) prohibits pacing into the atrial vulnerable period when a premature atrial contraction occurs during PVARP.
This is a non programmable value which is 125ms.
Premature atrial beat falls into PVARP, starting the API
The next Ap won’t be until the end of the API (125ms)-this can mean pacing slower than the LRL
Biotronik
Overdrive pacing
•rate increases by 8ppm for 20 cycles after each sensed atrial event that is not classified as a PAC (25% or > prematurity), in attempt to suppress atrial arrhythmias.
•At the end of the 20 cycles, the device will decrease pacing rate by 1ppm/cycle until an intrinsic event, and increase the pacing rate again by 8ppm and start a new 20 cycles up to a max rate of 120 or the USR.
•Overdrive pacing is deactivated when the mean atrial heart rate over a periods of 12 hours exceeds the average safety range (overdrive average rate limit = max overdrive rate – 10ppm).
•When the average HR falls below the average safety range, overdrive pacing is reactivated. If overdrive pacing is deactivated for a 3rd time because of this, overdrive pacing remains OFF permanently.



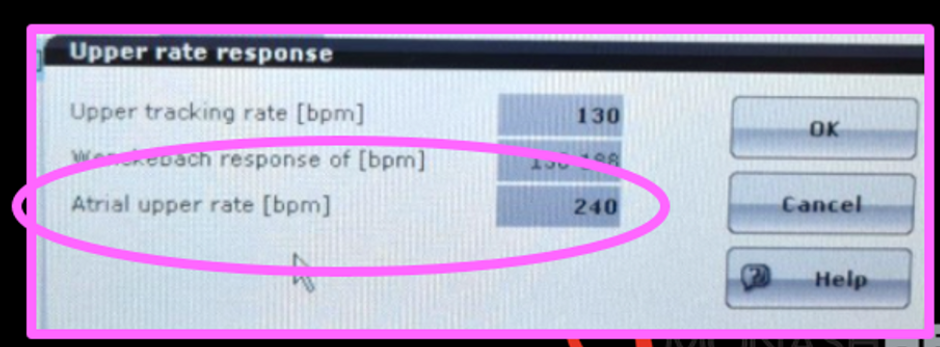
Atrial upper rate
•Prohibits pacing into the atrial vulnerable period when a premature atrial contraction occurs during PVARP.
•Premature atrial beat falls into PVARP, starting the atrial upper rate (AUR)
•The next Ap won’t be until the end of the AUR (250ms) -this can mean pacing slower than the LRL


Atrial ATP (aATP)
currently available in Amvia devices only
•allows for ATP in the atrium for atrial arrhythmias
•Therapy is delivered when the following criteria is met
-Rate detection is met (programmable (nominal 200bpm))
-36/48 beats fall in the detection zone
-stability of rhythm is confirmed (8 P-P intervals assessed: 3/8 are <200ms unstable/too fast (AF) -no delivery. if 5/8 P-P vary <= 40ms rhythm is stable)
-lead position check is confirmed (stable daily checks of pacing impedance and AP-Vs conduction times)
•Therapy is delivered as for stable rhythms
-output set at 6V @ 1.5ms
-S1 limited to 15 pulses
-sequences are programmable with the option of burst and/or ramp
-onset of ATP delivery can be programmed as a therapy delay (e.g., 1min after detection up to 24 hours after detection)
•Termination determined when 20/24 P-P < detection rate within 30 seconds after ATP delivery
•A maximum of 1000 ATPs can be delivered in a 30 day period
•aATP can be blocked when
-AF >48 hours
-HVR is detected within 30s after last aATP attempt
-daily lead check fails
•Can be programmed under parameters; tachycardia; therapy AT (stable)


Boston Scientific
Atrial preference pacing (APP)
•Promoted atrial pacing by increasing pacing rate (shortening the VA interval by 8ms) when a sensed atrial event occurs.
APP Search Interval
•at the end of the APP search interval (when the number of consecutive atrial events (As or Ap) equals the APP search interval), VA is lengthened by 8ms. This new VA is used until either an intrinsic As occurs (VA shortened again by 8ms) or until the end of the next search interval (VA increases again by 8ms).
APP Max rate
• the max pacing rate that the APP algorithm
•can achieve (cannot exceed max pace rate)



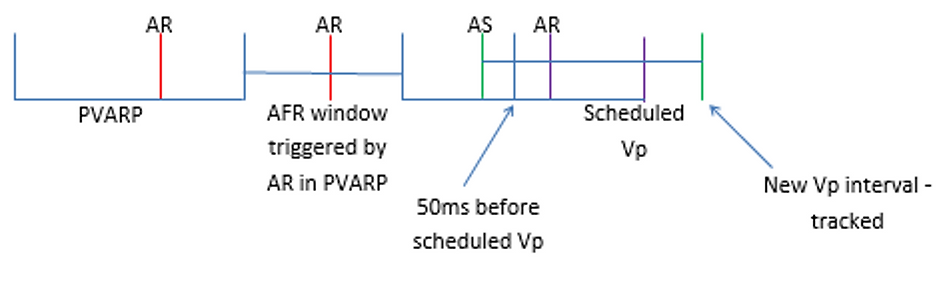
Atrial flutter response
•to prevent pacing into the atrial vulnerable period and to provide immediate fallback for atrial rates higher than the AFR programmable rate. (similar to NCAP). “blanked flutter”
•When AFR is programmed at 230bpm, a detected As inside PVARP or a previously triggered AF interval will start an AFR window of 230bpm (260ms). As inside AFR will be classified as AR, and not tracked. If another As occurs after the AFR window and >50ms before the scheduled Vp, the Vp will track the Vp. If As is detected with <50ms before the scheduled Vp, the A is not tracked and Vp occurs as scheduled. Continuous As in AFR window results in VDI type mode.
•AFR is only available in DDD & DDI. In DDI, AFR is automatically set to 230.


Medtronic
Post mode switch overdrive pacing (PMOP)
•designed to prevent early recurrence of AF after termination of an AF episode.



Atrial preference pacing
•designed to maximise AP percentage to promote a consistent activation site. When enabled, it can be programmed to provide continuous pacing that slightly exceeds the intrinsic sinus rate whenever the patient is not in an atrial tachyarrhythmia.
Max rate
•sets a maximum rate for APP
Interval Decrement
•the value by which the atrial pacing interval decreases (rate increases), in response to an AS event, per beat, to accelerate the pacing rate. (e.g., 30ms faster above the sinus rate)
Search beats
•the no. of consecutive paced beats required to decelerate the atrial rate in search of sinus activation.



Non competitive atrial pacing (NCAP)
•prohibits pacing into the atrial vulnerable period when a premature atrial contraction occurs during PVARP.
•Premature atrial beat falls into PVARP - AR
•Next scheduled beat is extended by 300ms with a shorter AV interval (30ms)



Reactive (atrial) ATP
•Allows for atrial antitachycardia pacing (ATP) during atrial arrhythmias
•Rhythm Change: changes in arrhythmias detected using both regularity & CL
•Subdivided into further sections: regular vs irregular & by A CL
•Time Interval: looks at changes in arrhythmias within an episode. This allows for reset of therapies (back to treatment 1). This option is only available in the 1st 48 hours of an episode.
Atrial ATP is suspended (until device in reinterrogated) if
•Ventricular rate accelerates (VCL <320ms or if during ATP)
•Atrial lead position check fails (auto feature of MDT)
Type of Atrial ATP
•Atrial Ramp: AOO at decreasing intervals based on the median of the last 12 PP intervals.
•Atrial Burst+: AOO S1 pulses followed by a shorter S2 & S3
•Atrial 50 Hz Burst: 50Hz (20ms)
All have VVI backup pacing








MINERVA
MINimizE Right Ventricular pacing to prevent Atrial fibrillation
Overall finding of pts with sinus bradycardia, pts with MINERVA programming had a lower incidence of permanent or persistent AF at 2 years post implant (15%) compared to MVP (25%) and DDD (26%) modes alone
•49% Relative reduction in cardioversions in MINERVA group vs DDD group
•52% relative reduction in AF related hospitalisations & ER visits in MINERVA group vs DDD group
Recommended programming
•MVP mode: AAI-DDD or AAIR-DDDR
•aATP therapies: on
•ARS: on (max 95)
•APP: on (max 95)
•PMOP: on (<5mins)
Microport
Overdrive
always pacing at a rate slightly above the intrinsic rate
increases pacing rate (up to a maximum programmable value) when a normal beat is sensed above present pacing rate &
•Each time a sinus P wave is detected the Atrial Escape Interval (EI) is shortened by 47 ms for 15 cycles
slowly decreases pacing rate when no sinus rate has been detected for 15 cycles.
Does not adjust for As beats that fall in atrial ectopic window


Pause suppression
The aim is to avoid the short - long cycle phenomenon after a PAC or PVC by shortening the atrial interval following a PAC or PVC
• i.e. by pacing in the compensatory pause.
Depending on whether it is a PVC or a PAC and the level of the PAC prematurity (how much faster than previous P waves) the algorithm calculates the timing of Escape Interval and AV Delay a little differently.
•After a PAC the Pause suppression algorithm initiates an intermediate interval.
•A late PAC also triggers an AV Delay.
•Upon PVC the Pause suppression algorithm synchronously paces the atrium.
Early PAC (P-PAC ≤ 50% last P-P)
•After an early PAC an intermediate escape interval is used:
The Intermediate EI = (PAC-P + PPmean8)/2
Example: EIinter = (420 + 900)/2 = 660 ms

Late PAC (P-PAC >50% last P-P)
•After a late PAC an intermediate escape interval is used and an AV Delay is triggered to minimize VV variation (AV Delay = previous AV Delay).
•EIinter = (PAC-P + PPmean8)/2

Post PVC
•When a PVC is detected the atrium is immediately (synchronously) paced to avoid retrograde conduction and the new atrial escape interval (EI) is smoothed
•EIinter = (PPmean8 - 31 ms)

PAC acceleration
The aim is to accelerate the atrial pacing rate after frequent PACs in order to decrease atrial refractoriness & to reduce PAC recurrence (considered to be one of the triggers of AF)
Acceleration
•Frequent ectopics is determined if there are less than 15 cycles between 2 PACs
•the algorithm accelerates the atrial pacing rate by approximately 5 bpm on each frequent PAC.
•example
•860ms/70bpm
•the 2nd PAC is “frequent” EI is shortened to 800 ms/75bpm

Deceleration
•When no more PACs are detected during 24 cycles, the rate deceleration is managed by the Smoothing algorithm.
•Note: When PAC Acceleration is programmed, the Smoothing will be automatically set to “Very Slow” if it was programmed OFF before
•the Escape Interval is lengthened by 16 ms every 8 cycles.

Max acceleration rate
•calculated by the algorithm to limit how much new frequent PACs can accelerate the rate
•rate can be accelerated up to a maximum rate calculated as follows:
•if the rate is less than 90 bpm (670 ms), the calculated minimum escape interval is 75% of the average of the last 8 cycles at the time of the first PAC.
•Otherwise, the calculated minimum escape interval is 75% of the average of the last 8 cycles plus 50 ms

A PAC counter counts the “level of frequency”
•any frequent isolated PAC increases the counter by +1
•multiple PACs are given gradually higher values (the first of a run +1, the second +2, the third +3 and so on) –
•a cycle without a PAC decreases by -1
•when the counter reaches 50 acceleration will be terminated
Smoothing will step down the rate until 15 cycles at basic/sensor rate or 15 sensed sinus P waves.







