Device algorithms to prevent RNRVAS
Summary
Abbott
•previously none
•PAC response (Gallant & Nutrina only)
Biotronik
•none
Boston
•None
Medtronic
•NCAP
Microport
•none
Medtronic
NCAP
Accessed under parameters; additional feature; non-comp atrial pacing
•Non-comp atrial pacing on off
•NCAP interval 300ms
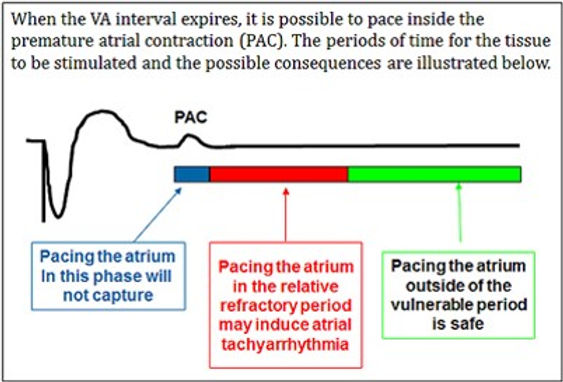
Non-Competitive Atrial Pacing (NCAP) is intended to prevent triggering of atrial tachycardias by delaying the scheduled atrial pace from occurring within the atrium’s relative refractory period
NCAP stops delivery of an atrial pace during the atrial refractory period because pacing in this vulnerable period may lead to an atrial arrhythmia. This can happen when the device is pacing at a high rate and a premature atrial contraction occurs during an atrial refractory period, followed quickly by an atrial pace.
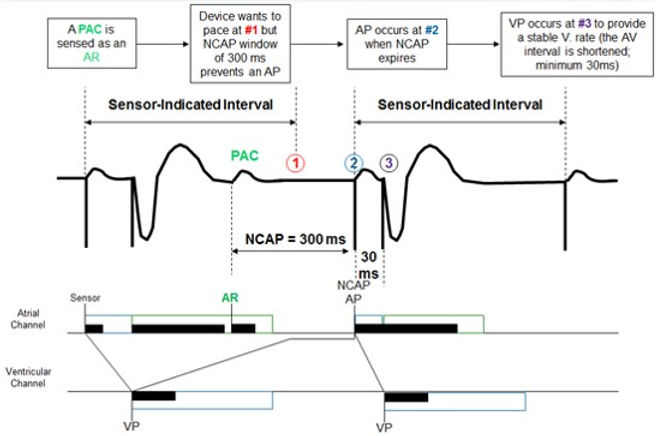
How NCAP affects atrial timing
•When NCAP is programmed to On, a refractory sensed atrial event falling in the PVARP starts a 300 ms NCAP period, during which no atrial pacing may occur:
•If a sensor-driven or lower rate pacing stimulus is scheduled to occur during the NCAP period, the VA interval is extended until the NCAP period expires.
•If no pacing stimulus is scheduled to occur during the NCAP period, timing is unaffected; pacing occurs at the end of the VA interval unless inhibited.
•An atrial refractory-sensed event occurring during the NCAP period starts a new NCAP period.
How NCAP affects ventricular timing
•When an atrial pacing stimulus is delayed by the NCAP operation, the pacemaker attempts to maintain a stable ventricular rate by shortening the PAV interval that follows.
•It will not, however, shorten the PAV interval to less than 30 ms.
Considerations
•Non-Competitive Atrial Pacing becomes operational in DDDR and DDD pacing modes. It maintains an interval of 400 milliseconds for one pacing cycle whenever a PVC Response or a PMT Intervention occurs. Its availability is also dependent on the following:
•When Mode Switch is programmed On, NCAP operations are temporarily disabled if the pacemaker mode switches to the non-atrial tracking mode. The NCAP feature is re-enabled upon return to the atrial tracking mode.
•Even when NCAP is programmed Off, the NCAP operation is invoked automatically for cycles on which PMT Intervention or PVC Response operations occur.
•When a relatively high Lower Rate and long PVARP are programmed, NCAP operation may result in ventricular pacing slightly below the Lower Rate.


Abbott
PAC response
Not available in most current devices.
Only available in Gallant and Nutrina devices.
Accessed under parameters; refractory & blanking; additional settings' PAC response
•PAC response on off
•PAC response 330ms (200-400ms)
Essentially works very similar to Medtronic NCAP algorithms (in depth details have not been made transparent to the public at this stage)
When PAC response is programmed to On, a refractory sensed atrial event falling in the PVARP starts a PAC response interval (nominal 330ms) during which no atrial pacing may occur
When PAC response occurs 16 times in a row, an EGM is stored as PAC response
Since being established in 2000, PMTs & RNRVAS has been known for an unparalleled commitment to customer satisfaction. It’s this standard of excellence that has provided the impetus for us to grow into the business we are today. For more information about the products and services we provide, reach out today.




