Lead Impedances
•The impediment to current flow in the pacing system
•The opposition of flow of electrical current through a conductor
Contributing factors to impedance include
•Lead conductor resistance
•Electrode resistance
•Electrode polarisation
Hose example
•Water is the voltage (set to a certain level)
•The nozzle is the resistance/impedance
The flow of the water through the hose is the current
•When there is a lot of
resistance, the flow decreases
•When there is low resistance
(nozzle loosened) flow of water
increases (increase current)

Ohms Law
The relationship between voltage (V), current (I) & resistance (R) is demonstrated by Ohms Law

Ohms Law example

Ohms Law example

Normal impedance values
Impedances ranges vary from brand to brand, model to model
•Standard pacing lead impedances 200-1200 Ω
•high impedance leads 800-1800 Ω
•thin line leads 200-900 Ω
•high voltage leads 15-100 Ω
Drop in impedance
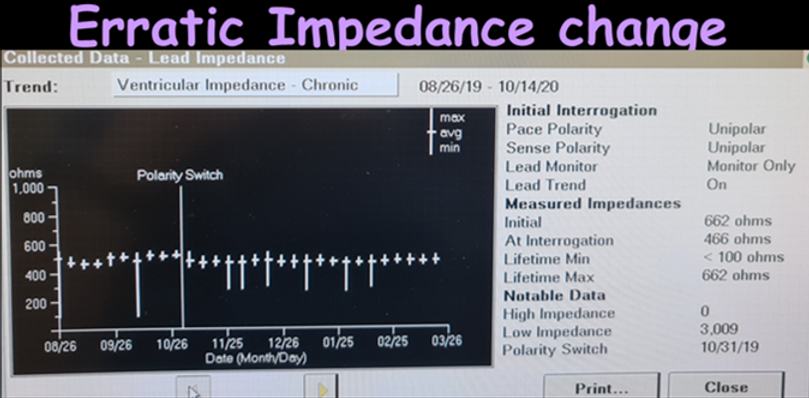
Erratic low impedance
•Intermittent signs of insulation breach
Sudden decrease
•Established insulation breach
•Lead dislodgement
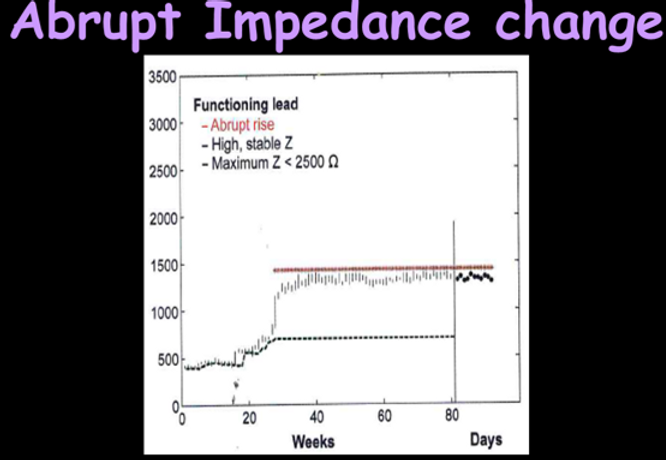
Increase in impedance
Slowly increasing
•Development of exit block
•Development of lead fracture
Erratic high impedance
•Intermittent signs of fracture
•Header/connector issue
Sudden increase
•Established lead fracture
•Lead dislodgement