
Question 1
Which factors will have the largest effect on battery longevity?
A lead resistance, output programming, rate response on
B output programming, rate response on, sensitivity programming
C sensitivity programming, rate response on
D rate response on, output programming, AV search algorithm on
Question 2
What may occur if there is a ventricular lead fracture?
Chose which is incorrect.
A high impedance
B noise
C pacing inhibition
D low impedance
E lower pacing percentage
Question 3
A single chamber pacemaker is set with an output of 2V @ 0.4ms, with a sensitivity of 2mV. If an R wave was measured at 1.5mV, how would we program the device to allow appropriate functioning?
A Increase output to 3V @ 0.4ms
B Decreased output to 0.75V @ 0.4ms
C Decrease sensitivity value to 0.75mV
D Increase sensitivity value to 3mV
Question 4
Which one of the following has the weakest indication for device implant for sick sinus syndrome?
A Symptomatic sinus bradycardia with documented sinus pauses
B Syncope with unexplained origin with sinus node dysfunction shown in EP study
C Symptomatic sinus bradycardia as a result of drug therapy required for a medical condition
D Symptomatic chronotropic incompetence
Question 5 (4 continued)
Are the answers for number 8 all indications for pacemaker implantation?
A yes
B no
Question 6
Which one of the following has the weakest indication for device implant for AV node dysfunction?
A Pacemaker syndrome or hemodynamic compromise due to 1st degree AV block
B VT/VF occurring presumably as a result of 2/3rd degree AV block
C Symptomatic 2/3rd degree AV block as a result of drug therapy required for a medical condition
D Post surgical 2/3rd degree AV block
Question 7 (6 continued)
Are the answers for number 10 all indications for pacemaker implantation?
A yes
B no
Question 8
Which class does spontaneous neurocardiogenic syncope fall into for device implantation indication?
A Class I
B Class IIa
C Class IIb
D Class III
Question 9
What does the ECG in figure 1 show?
A failure to capture
B undersensing
C Oversensing
D appropriate DDD function
E appropriate VVI function

Figure 1
Question 10
What can we determine from the ECG in figure 2 for a patient who has a dual chamber pacemaker (DDD)?
A Appropriate atrial sensing and capture
B appropriate atrial capture and ventricular sensing
C Appropriate atrial capture but no ventricular capture
D appropriate ventricular sensing and pacing

Figure 2
Question 11
Mr Johnson came in for a routine 6 month device check for his dual chamber pacemaker. Compared to his last pacemaker check, his ventricular pace percentage has increased dramatically. Which of the following options does not explain why this may have occurred?
A Loss of atrial capture
B increase in ventricular threshold
C ventricular undersensing
D Mr Johnson has developed significant AV block
Question 12
A patient has a dual chamber pacemaker, and has presented in AF at clinic today. Which is the most appropriate mode to test the ventricular threshold in?
A DDD
B VDD
C DDI
D DOO
Question 13
Which of the following would not help assess whether atrial loss of capture has occurred in a threshold test?
A loss of AV conduction
B atrial reset
C loss of P wave on ECG
D Atrial EGM appears smaller
Question 14
If a lead had an insulation breach but remained intact, what is the most likely finding on the impedance trend?
A low impedance
B high impedance
C normal impedance
D both high and low impedance
Question 15
On which occasion does the ventricular blanking period occur?
A After a ventricular sensed beat
B After a ventricular paced beat
C After an atrial paced beat
D After an atrial sensed beat
E Both A and B
Question 16
If a device is programmed at DDD 60-140, with a PVARP of 350ms and an AV delay of 250ms, what is the point at which it will lose 1:1 AV synchrony?
A 140 bpm
B 92 bpm
C 130 bpm
D 100 bpm
Question 17
Which of the following options would assist in maximising the upper rate behaviour (allow for 1:1 AV synchrony)?
A Utilising rate responsive AV delays
B Utilising rate responsive PVARP
C Shortening PVARP
D Shortening AV delays
E Both A and B
F All of the above
Question 18
A dual chamber pacemaker programmed to DDD mode recognises which of the following as a PVC?
A Atrial pace coincident with a PVC
B Atrial pace with a PVC sensed in the safety pace window
C Loss of atrial capture followed by a junctional beat
D Sinus beat with a loss of atrial sensing.
Question 19
A dual chamber pacemaker is programmed DDD with a lower rate limit of 50 bpm, an upper rate limit of 125, an AV delay of 175ms that is reduced by 25 ms at an atrial rate of 100 bpm, and an post ventricular atrial refractory period of 300ms. During a stress test the atrial rate is 128 bpm, the ventricular response is most likely to be which of the following?
A 1:1 AV conduction
B 2:1 AV block
C 3:1 Sinoatrial block
D pseudo Mobitz type II AV block
E pseudo Wenckbach AV block
Question 20
A patient with complete heart block has a dual chamber pacemaker programmed to DDDR mode. Which of the following is most likely to occur at sensor indicated rates above the maximum tracking rate?
A AV sequential pacing
B crosstalk
C mode switching
D pseudo-wenckebach 2nd degree AV block
E 2:1 AV block
Question 21
Which pacing interval is designed to prevent T wave oversensing?
A Atrial blanking period
B A-V interval
C PVARP
D Ventricular blanking periods
E Ventricular refractory period
Question 22
Which pacing interval is designed to prevent cross talk?
A Atrial blanking period
B PVARP
C Ventricular blanking period
D Ventricular refractory period
Question 23
If the pacemaker output voltage is 5V and the measured lead resistance is 330 ohms, then the current that flows out of the pacemaker in the heart is
A 1.65 mA
B 15.15 mA
C 66 mA
D 10 mA
Question 24
What does figure 3 show?
A atrial oversensing
B atrial undersensing
C ventricular oversensing
D ventricular undersensing

Figure 3
Question 25
What is happening in figure 4?
A PMT
B upper rate behaviour
C upper sensor rate behaviour
D atrial fibrillation
E pacemaker malfunction

Figure 4
Question 26
What does the EGM in figure 5 demonstrate?
A AF
B SR
C VT
D pacemaker malfunction
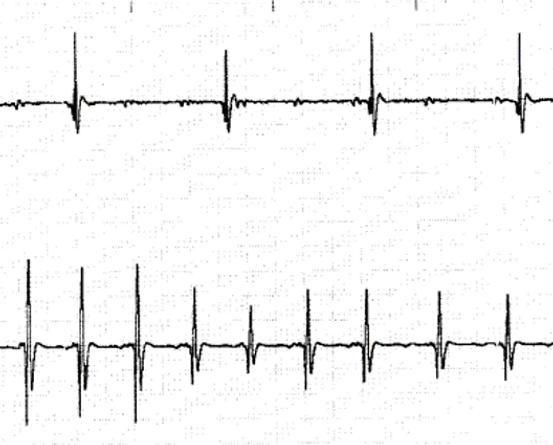
Figure 5
Question 27
Temporary programming of VVI 30 is utilised in figure 6. What rhythm does the strip show?
A Sinus rhythm with 1st degree AV block
B Atrial fibrillation
C junctional escape
D Sinus bradycardia with 1st degree AV block
E sinus rhythm with complete heart block

Figure 6
Question 28
What is the best initial intervention for the ECG abnormality shown in Figure 7?
A increase ventricular sensing
B Turn AV hysteresis off
C Lengthen AV delay
D Increase ventricular pacing output
E Replace the ventricular lead

Figure 7
Question 29
The atrial rate histogram shown in figure 8 is obtained during a PPM interrogation. The corresponding ventricular histogram shows no rates lower than 70 bpm. Which of the following is the most likely explanation for this finding?
A noise response
B PACs
C PVCs
D Rate drop response
E Sleep hysteresis

Figure 8
Question 31
Which patients pacemaker will last the longest (all 100% paced)?
A Pt 1: LRL 60 ppm output: 5V impedance 500 ohms
B Pt 2: LRL 60 ppm output: 2V impedance 500 ohms
C Pt 3: LRL 60 ppm output 2V impedance 300 ohms
D Pt 4: LRL 70 ppm output 2V impedance 500 ohms
Question 32
The advantage of a bipolar lead is
A they are less susceptible to EMI
B they cause muscle stimulation
C small battery/IPG cases
D diameter of lead is smaller
Question 33
If an external pacemaker is set to a sensitivity setting of 5mV and some R waves go undersensed, then you should do the following
A decrease sensing to 7mV
B increase sensing to 10 mV
C increase sensing by lowering sensitivity to 2.5 mV
D move the sensitivity control to asynchronous
Question 34
A SSI pacemaker is one that
A senses and paces in either the atrium or ventricle
B senses the atrium and paces the ventricle
C should not be used for atrial application
D is contraindicated in the presence of AF
Question 35
Which of the following is/are not factor(s) which influence pacemaker longevity?
A output voltage
B lead resistance
C Pulse duration
D blanking
Question 36
A pacemaker that paces and senses only in the ventricle and is inhibited by spontaneous ventricular activity is designated
A VAT
B VVT
C VVI
D VOO
E VDD
Question 37
All of the following functions are programmable in both VVI and DDD pacemakers except
A AV interval
B sensitivity
C Output
D Refractory
Question 38
In a bipolar pacing ventricular pacemaker
A the cathode is in the heart and the anode is in a remote location
B The anode is in the heart and the cathode is in a remote location
C both the anode and the cathode are in the heart
D neither the anode nor the cathode is in the heart
Question 39
Each of the following statements regarding the DDI mode of pacing is true except:
A the blanking period follows delivery of the atrial stimulus
B the upper rate is controlled by the duration of the atrial refractory period
C The pacemaker senses in the atrium
D The pacemaker does not track intrinsic atrial activity
Question 40
Which would be the best option to manage the rhythm in Figure 9?
A Increase ventricular sensitivity to a higher value
B Increase ventricular output
C Increase PVARP
D Increase ventricular blanking period

Figure 9
Question 41
What would one program to correct the problem demonstrated in Figure 10
A atrial sensitivity
B PVARP
C ventricular output
D ventricular sensitivity

Figure 10
Question 42
The circled beat in figure 11 best describes what?
A fusion
B high output back up pulse
C pseudofusion
D intrinsic

Figure 11
Question 43
The P wave measurements in figure 12 are most likely explained by which of the following
A normal P wave variation
B the development of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation
C the development of paroxysmal atrial flutter
D the development of paroxysmal atrial tachycardia

Figure 12
Question 44
Which of the following is demonstrated in figure 13?
A DDI pacing
B DDD pacing
C DDD with rate adaptive AV delay
D DDD with loss of atrial sensing

Figure 13
Question 45
What is the most likely interpretation of the interval plot in figure 14
A sinus to AF to sinus
B sinus to atrial flutter to sinus
C sinus to VT to sinus
D sinus to VF to sinus

Figure 14
Question 46
Each of the following is typically interpreted as a PVC by a pacemaker except
A loss of atrial capture followed by ventricular capture
B a junctional beat
C the second deflection of a double sensed R wave
D a normal sinus beat with the p wave falling in PVARP
Question 47
The DDD featured below is programmed to a based rate of 50. The ECG in Figure 15 demonstrated
A normal pacemaker function
B atrial oversensing
C ventricular oversensing
D Atrial and ventricular oversensing

Figure 15
Question 48
What is the voltage measurement of a pacing system with an impedance of 500 ohms, current of 5mA, pulse width 0.4ms and a pacing rate of 60ppm
A 1.0 V
B 2.5 V
C 5.0 V
D 5.5V
Question 49
What is the estimated battery service life of a pacemaker with a 1.0 Amp-hour battery and a 20microamp current drain?
A 4 years
B 5 years
C 5.7 years
D 10 years
Question 50
In which phase of the action potential does the extracellular transmembrane potential become more negative than the intracellular potential?
A 0-1
B 2
C 3
D 4





