
Question 1
Based on research findings, which of the following is most likely to have the best DFT?
A RV coil anode, can cathode, monophasic waveform
B RV coil cathode, can anode, monophasic waveform
C RV coil anode, can cathode, biphasic waveform
D RV coil cathode, can anode, biphasic waveform
Question 2
A shock may result in all of the following except
A Pain
B Ventricular arrhythmia induction
C Successful reversion to sinus rhythm
D Syncope
E Myocardial injury
Question 3
Factors affecting efficacy of ATP include all of the following except
A whether the VT is non ischemic or ischemic in origin
B distance of VT from the pacing lead
C duration of the ventricular arrhythmia
D the type of the VT
E the speed of the VT
Question 4
A patient has exercise induced VT with sinus rates that crossover into the VT detection zone. One would most likely choose the following criterion/criteria to optimize specificity for VT detection in this patient?
A rate only
B rate and sudden onset
C rate and interval stability
D rate and morphology discrimination
Question 5
Which of the following factors tends to be the most common denominator as to whether or not there are EMI/device interactions?
A duration of exposure
B refractory periods
C distance from the EMI
D sensitivity setting
Question 6
What is/are the reason/s for performing a DFT?
A Assessing the appropriate sensing and detection of VF
B Confirmation of the integrity of the ICD system
C Establishing an adequate saftey margin for defibrillation
D A and C
E A, B and C
Question 7
Which of the following trials demonstrated that ATP therapy could decrease shocks by 77% without risk of acceleration, deaths and time to termination?
A AVID
B CASH
C MIRACLE
D PainFree II
Question 8
Which of the following would rule out VT?
A V rate > A rate
B V rate = A rate
C V rate < A rate
D none of the above
Question 9
The stored EGM featured in Figure 1 was downloaded from a SR ICD after he received a shock. The implant was due to Long QT. What device programming feature could have possibly prevented this episode?
A non competitive atrial pacing
B mode switching
C rate smoothing
D rate response

Figure 1
Question 10
Appropriate shocks can be associated with all of the following except
A lower quality of life
B Higher mortality
C PTSD
D Decrease in charge time
E Decrease in battery voltage
Question 11
This dual chamber ICD patient presented to the ED department with palpitations. The device was interrogated and the episode in figure 2 was downloaded and printed for analysis. The patient did not receive therapy because
A the onset SVT detection algorithm saw this as a gradual increase
B PR logic classified this rhythm as a sinus tach
C it was undersensed by the device
D the vt did not meet the detection criteria
Figure 2

Question 12
Which of the curves in figure 3 best approximated the most common ICD battery discharge curve?
A A
B B
C C
D D
Figure 3

Question 13
Mr Farrell had 5 shocks for VF when he presented with an anterior STEMI. His baseline ECG shows sinus rhythm 80bpm with normal QRS complex. Which of the following is the most appropriate management of this patient?
A Single chamber primary prevention ICD
B Dual chamber primary prevention ICD
C Single chamber secondary prevention ICD
D Dual chamber secondary prevention ICD
E Medical management
Question 14
A 20 year old male is implanted with a dual chamber ICD due to HCM and sustained VT of 165bpm. The pt received 5 shocks and presented to ED. Interrogation demonstrated the EGM in figure 4. Interrogation reveals that preceding the shocks, there were 3 ATP attempts. None of the delivered therapies altered the tachycardia. The best management of this patient would be
A implant a higher output device
B turn on rate stabilization
C raise the VT rate cutoff
D activate the morphology discriminator
Figure 4

Question 15
Which of the following may likely occur as a result of reversing the distal and proximal shock coils in the header of an integrated defibrillation lead system?
A may result in a change of therapy efficacy
B would be the same as programming reverse polarity
C would get atrial pacing from the ventricular channel
D oversensing
E Both A and D
Question 16
Which is the electrical circuit that converts a signal with both positive and negative components into a signal with only one component?
A resistor
B rectifier
C diode
D capacitor
Question 17
Mrs Claus presented with increasing shortness of breath. An echo was requested and demonstrated dilated cardiomyopathy with moderate LV dysfunction and an LVEF of 32%. Her baseline ECG shows sinus bradycardia 50bpm with normal QRS complex and her angiogram demonstrated no significant artery narrowings. Which of the following is the most appropriate management of this patient??
A Single chamber primary prevention ICD
B Dual chamber primary prevention ICD
C Single chamber secondary prevention ICD
D Dual chamber secondary prevention ICD
E Medical management
Question 18
If the patient with the settings in figure 5 went into AF with a ventricular response >200 bpm the ICD would?
A withhold therapy due to stability
B withhold therapy due to onset
C deliver therapy because the arrhythmia is in the VF zone
D deliver an atrial burst

Figure 5
Question 19
Mr Sully was treated with 1xATP for the arrhythmia shown in Figure 6. The SVT discriminiators were programmed as follows, RHYTHM ID ON: Atrial tachyarrhythmia discrimination ON, Afib rate threshold 170bpm, Stability 20ms, rhythm match 94%, onset 10%. Based on the Summary, do any changes need to be made to Mr Sullys programming?
A No. This episode was correctly discriminated as VT
B If V had been = A, therapies would have been withheld due to onset, thus onset should be turned off.
C If V had been = A, therapies would have been withheld due to morphology, thus morphology should be turned off.
D If V had been = A, therapies would have been withheld due to stability, thus stability should be turned off
Figure 6

Question 20
A patient with a Medtronic ICD presented to clinic for a regular check. The morphology was reviewed and is shown in Figure 7. What would you do next?
A Turn off all SVT discriminators
B Update morphology and change vector if necessary
C Lower VT detection zone
D No changes
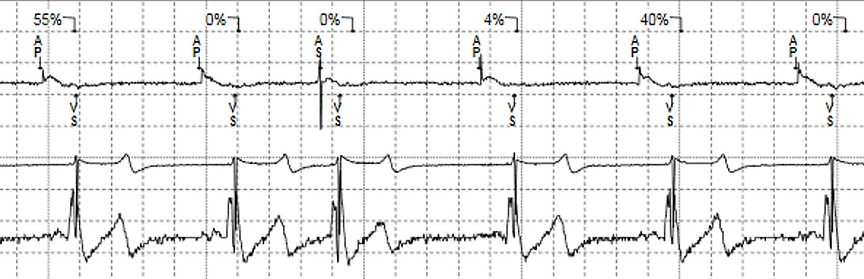
Figure 7
Question 21
Mrs Spencer is implanted with a dual chamber ICD for secondary prevention. She has underlying sinus rhythm with a history of atrial fibrillation. Which of the following would be the most optimal SVT discriminators to be turned on?
A onset, stability, A/V relationship and morphology
B morphology, A/V relationship and stability
C onset, stability and morphology
D A/V relationship, morphology, chamber onset and stability
Question 22
What do Flecainide and Verapamil have in common?
A They are both class I drugs
B They are both class IV drugs
C They can both increase DFT
D They can both decrease DFT
E None have an effect on DFT
Question 23
Which of the following sensing settings can help minimise oversensing T waves?
A Refractory periods
B TW discrimination
C low sensitivity value
D Decay delay
Question 24
Mr Smith was implanted four week ago with a dual chamber ICD. He was admitted to ED for having 31 shocks in 3 hours. His EGMs are in figure 8. The reason for his shocks were because of
A lead dislodgment
B VT storm
C failure of SVT discriminator
D lead fracture
Figure 8

Question 25
A dual coil integrated bipolar transvenous ICD lead has its sensing circuit between the
A distal coil and proximal coil
B tip electrode and proximal coil
C proximal coil and can
D tip electrode and distal coil
Question 26
A patient presented with a syncopal event. On interrogation the EGM in Figure 9 was found. What is the next step
A Decrease sensitivity to a lower value
B Shorten detections
C No programming changes
D Turn SVT discriminators on
E Suspend ICD therapies and organise for a lead replacement
Figure 9

Question 27
Which of the following is a class III indication for ICD implantation
A VT not due to a reversible cause
B severe symptoms attributable to VT while patient awaits heart transplant
C incessant VT
D NSVT, previous MI, + EP study
Question 28
Which of the following is the most significant advantage of reducing inappropriate shocks?
A improving quality of life
B increasing device longevity
C reducing the number of proarrhythmias
D reducing mortality
Question 29
Which of the following is most likely to trigger EOL in an ICD
A capacitors charging
B a high % of bradycardia pacing
C interrogation
D ATP pacing
Question 30
The EGM in Figure 10 demonstrates which of the following?
A normal ICD function
B TWOS
C R wave double counting
D farfield oversensing
Figure 10

Question 31
Which of the following is not a method of inducing VF?
A Shock on T
B DC fibber
C Ventricular sense response
D Burst pacing
Question 32
A patient is having an ICD battery change with a DF1 lead/can. The doctor notices an insulation problem on the pace/sense portion of the lead. A new pace/sense lead is implanted and connected to the ICD. A DFT is performed and a loud pop occurs in the pocket. What can one expect to find?
A Low HV impedance
B High HV impedance
C low pacing impedance
D high pacing impedance
Question 33
A post MI patient has an echo showng an EF of 29%. He has never had any evidence of VT/VF or syncope. Based on MADIT II criteria he was implanted with a single chamber ICD. After 7 years of follow up his device reached ERI. He has never reciveed any therapy from his device. Based on this information, the EP will most likely recommend the device be
A explanted and not replaced
B deactivated and not replaced
C changed out for a dual chamber ICD
D changed out for a single chamber ICD
Question 34
Percent tilt on ad ICD waveform refers to the
A relationship between charge time and DFT
B decrease in tissue impedance as a shock is delivered
C shock delivery efficiency of a capacitor
D decline in leading edge voltage at the time of truncation
Question 35
A class III HF pt was implanted with a dual chamber CRTD. The stored EGM in figure 11 shows 2 ATP attempts. The 1st attempt would be considered to have done what to the patients tachycardia?
A terminated the sinus tachycardia
B accelerated to fast VT
C slowed out of the VT zone
D ineffective non-conversion
Figure 11

Question 36
The 2nd attempt in figure 9 would be considered to have done what to the patients tachycardia?
A terminated the sinus tachycardia
B accelerated to fast VT
C slowed out of the VT zone
D ineffective non-conversion
Question 37
Which of the following is not a determining factor when choosing between a single coil or a dual coil tachycardia pacing lead in a child?
A venous access
B heart size
C programmable vectors
D electrode positioning
Question 38
Which of the following is the most accurate interpretation of the scatter plot on the diagram in figure 12?
A VT, ramp, FVT, shock, termination
B FVT, VT, stabilization, VF, termination
C SVT, burst, acceleration, termination
D FVT, burst, acceleration, termination
Figure 12
Question 39
A patient came to a routine clinic and had figure 13 in their episode list. What would you do next?
A Advise the patient to avoid large magnet fields
B Reprogram the ventricular sensing from unipolar to bipolar sensing
C Turn therapies off immediately and get patient admitted to hospital
D Perform troubleshooting movement manoeuvres
E Review trend data
Figure 13

Question 40
Which of the following options most likely explains the differences between the top and bottom strip in figure 14?
A the electric shaver was turned OFF
B an intermittent fracture
C EMI source turned OFF
D polarity programming
Figure 14

Question 41
The image in Figure 15 demonstrates what?
A A subcutaneous array
B A DF1 lead
C A DF4 lead
D An LV IS4 lead

Figure 15
Question 42
Figure 16 shows an episode which was treated with a shock. Which of the following is incorrect?
A There are more V’s than As
B ATP may have been successful at terminating the arrhythmia
C The morphology is not a match
D SVT discriminators would have been applied

Figure 16
Question 43
Mr Paul has 3 zones programmed for his VT therapies as described below.
Zone Rate Detection Therapy
VT1 150 bpm 15 MONITOR ONLY
VT2 175 bpm 15 3 burst (scan-88%), 4 x 40J shock
VF 200 bpm 15 TP while charging, 6 x 40J shock
What programming changes would you suggest to the physician after seeing the episode in Figure 16? Choose the most correct answer.
A No programming changes.
B Increase the VF zone to a higher rate
C Lengthen detections on VT2 zone
D Turn off SVT discriminators
Question 44
Mr Lock has a VT which is 200 bpm? Based on the settings in Figure 17, what will the 1st ATP look like?
A 243ms, 243ms, 243ms, 243ms, 243ms, 243ms, 243ms, 243ms, 243ms, 243ms,
B 243ms, 243ms, 243ms,
C 243ms, 233ms, 225ms
D 264ms, 264ms, 264ms, 264ms, 264ms, 264ms, 264ms, 264ms, 264ms, 264ms,
Figure 17

Question 45
The patient in figure 18 has felt some palpitations during this episode. Which of the following would be the best course of action?
A keep device as programmed
B suggest programming in a more aggressive ATP therapy
C suggest delaying ATP therapy
D suggest programming a low energy shock as the 1st therapy
Figure 18

Question 46
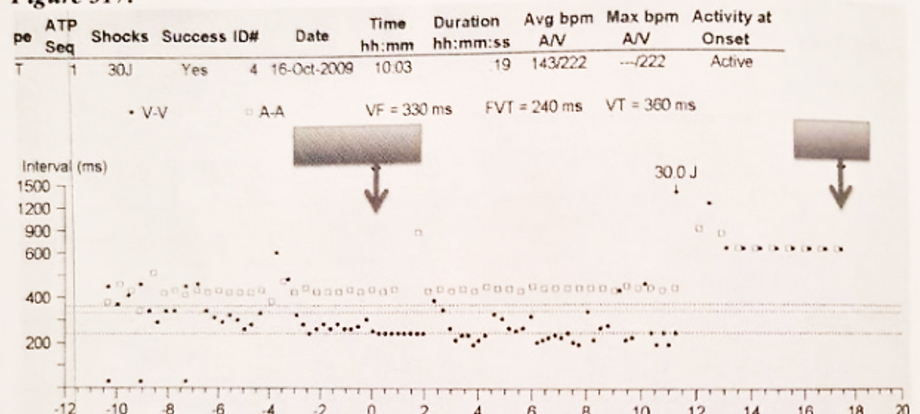
Mr Dero has a VT episode in the VT2 zone with a rate of 200bpm. Based on the settings in Figure 19, what will the 2nd round of ATP look like?
A There is only one round of ATP programmed on
B 255ms, 255ms, 255ms, 255ms
C 255ms, 255ms, 255ms, 255ms, 255ms, 255ms, 255ms, 255ms
D 245ms, 245ms, 245ms, 245ms, 245ms, 245ms, 245ms, 245ms
E 255ms, 255ms, 255ms, 255ms, 255ms, 255ms, 255ms, 255ms, 255ms
F 245ms, 245ms, 245ms, 245ms, 245ms, 245ms, 245ms, 245ms, 245ms
Figure 19

Question 47
The stored EGM in figure 20 is from a patient with a documented history of exercise induced monomorphic VT. The event in figure 1 was collected at a time when the patient was exercising. From the stored information you can determine that the
A device responded appropriately
B device delivered inappropriate therapy
C programmed detection enhancement failed
D device experienced far field oversensing
Figure 20

Question 48
What is shown in figure 21?
A T wave oversensing
B P wave oversensing
C R wave double counting
D Far field R wave
E Appropriate pacing and sensing
Figure 21

Question 49
What would you do about the EGM shown in Figure 21?
A Increase RV output
B Increase LV output
C Increase Atrial output
D Extend ventricular refractory period
E Increase ventricular sensitivity value to a higher number
Question 50
What does the image in Figure 22 demonstrate?
A Appropriate sensing, detection and treatment of VF
B Appropriate sensing, and detection VF
C Appropriate induction, sensing and treatment of VF
D Appropriate induction and sensing of VF
Figure 22






