
Question 1
Which of the following will not affect a PMT?
A reprogramming device to non-tracking mode
B decreasing PVARP
C putting a magnet over the device
Question 2
What are the ideal values for a V lead at implant?
A Threshold <1V @ 0.5ms and sensing >5mV
B Threshold >1V @ 0.5ms and sensing <5mV
C Threshold <2V @ 0.5ms and sensing >5mV
D Threshold <2V @ 0.5ms and sensing <5mV
Question 3
If the doctor at implant is unsure of how to connect the pacing testing cables at implant, how would we advise to set it up?
A Bipolar: black to ring, brown to tip. Unipolar: brown to skin, black to tip
B Bipolar: black to ring, brown to tip. Unipolar: black to skin, brown to tip
C Bipolar: brown to ring, black to tip. Unipolar: brown to skin, black to tip
D Bipolar: brown to ring, black to tip. Unipolar: black to skin, brown to tip
Question 4
Which of the following algorithms would not help if were trying to encourage intrinsic AV conduction in a dual chamber pacemaker?
A Decreasing AV delays
B Changing mode to from DDD to AAI-DDD
C Turning on AV search hysteresis
D Turning on IRS plus
E Turning on VIP
Question 5
Which of the following should we check at generator change in the old battery prior to starting the case? Choose the incorrect answer
A Lead type is compatible with new pacemaker
B Polarity switch is ON
C RR is turned OFF
D Current lead/s are functioning appropriately
E Patients underlying rhythm
Question 6
How will a Medtronic pacemaker function if a magnet is placed on it
A No response
B ICD therapies will be suspended
C It will pace asynchronously at 100 ppm
D It will function in DDD at the set base rate
E It will pace asynchronously at 85 or 65
Question 7
What could possibly occur for the patient with the xray in figure 1?
A noise
B inappropriate tracking
C change in impedance
D all of the above
E A and C only

Figure 1
Question 8
A PMT may be initiated by which of the following?
A loss of atrial capture
B ventricular premature beat
C loss of atrial sensing
D All of the above
E A and B only
Question 9
The ECG in figure 2 was recorded the day after implantation of a single chamber ventricular pacemaker. What can we conclude about the implant based on this ECG.
A Successful implantation
B Loose set-screw
C Lead insulation breach
D Lead perforation

Figure 2
Question 10
Which of the following is incorrect
What could occur as a result of what is shown in the xray shown in figure 3
A loss of capture
B high impedance
C low impedance
D normal impedance
E noise

Figure 3
Question 11
A patient is having a dual chamber pacemaker inserted, but is in atrial fibrillation today. How would we test the atrial lead?
A Threshold, sensing and impedance as usual
B Sensing only
C Sensing and impedance while pacing in AAI
D Sensing and impedance while pacing in AOO
Question 12
Which mode would be most appropriate for a patient who has sick sinus syndrome with 1st degree atrioventricular block?
A DDD(R) with long AV delays
B DDD(R) with short/normal AV delays
C AAI/ADI(R) based mode with DDD mode switch
D VVI(R)
Question 13
Which mode would be the most appropriate for a patient with sinus rhythm with permanent complete heart block?
A DDD(R) with long AV delays
B DDD(R) with short/normal AV delays
C AAI/ADI(R) based mode with DDD mode switch
D VVI(R)
Question 14
Which lead access is more likely to result in a pneumothorax?
A Cephalic
B Subclavian
C Axillary
Question 15
The principal purpose of a PVARP in the dual chamber pacemaker timing is prevention of which of the following?
A atrial sensing of a retrograde atrial impulse
B atrial sensing of the ventricular pacing stimulus
C ventricular sensing of the T wave
D ventricular sensing of the atrial pacing stimulus
Question 16
How may a pacemaker behave at EOL
A deliver no output
B runaway pacemaker
C may be unable to interrogate
D A and C only
E all of the above
Question 17
A woman with normal ventricular function undergoes an AV node ablation after having a PPM inserted for AF with RVR. Which of the following is the most likely reason for setting the initial lower rate limit to 80 ppm?
A Avoid ventricular arrhythmias
B Decrease mitral regurgitation
C Decrease ventricular remodelling
D improve cardiac output
E regularise the ventricular rate
Question 18
What does the EGM in figure 4 show?
A PMT
B normal pacemaker function
C competitive atrial pacing
D atrial lead failure

Figure 4
Question 19
How would we program around the issue in Figure 4?
A shorten AV delay
B lengthen AV delay
C shorten PVARP
D lengthen PVARP
E both A and C
F both B and D
Question 20
What type of device is shown in Figure 5?
A single chamber pacemaker
B dual chamber pacemaker
C single chamber defibrillator
D dual chamber defibrillator
E biventricular pacemaker
F biventricular defibrillator

Figure 5
Question 21
What type of device is shown in Figure 6?
A single chamber pacemaker
B dual chamber pacemaker
C single chamber defibrillator
D dual chamber defibrillator
E biventricular pacemaker
F biventricular defibrillator

Figure 6
Question 22
When connecting a unipolar pacemaker to the lead in the patient
A tighten both set screws
B place the pacemaker in the pocket to check pacing
C always implant so the lead comes off counter clockwise
D verify pacing before placing pacemaker in the pocket
Question 23
Hysteresis is
A a lower rate for activity pacemakers
B the interval the pacemaker waits after a sensed beat before pacing
C the interval (rate) after a paced beat
D not useful for saving energy
Question 24
A doctor from the Neurology/stroke ward has asked for a pacemaker check on the patient with the device shown in Figure 7 to investigate AF burden. Would a device check here be useful?
A Yes
B No
Figure 7

Question 25
The most common cause of permanent downgrading of the DDD mode to VVI mode is
A atrial lead fracture
B atrial undersensing
C Chronic AF
D paroxysmal AF
E too high a threshold for atrial pacing
Question 26
A high cell impedance noted on a pacemaker check indicates which of the following?
A Battery depletion
B lead fracture
C lead dislodgment
D loose set screw
E lead insulation failure
Question 27
Which of the following algorithms is not useful in minimising symptoms of vasovagal syncope?
A Hysteresis
B Closed Loop Stimulation
C Ventricular rate regulation
D Rate drop response
Question 28
Which of the following risk factors are NOT useful for deciding on whether someone should be on blood thinners?
A Low blood pressure
B Previous stroke
C Atrial fibrillation
D Age
Question 29
Which of the following algorithms are not useful in minimising atrial fibrillation
A Atrial preference pacing
B Rate fading
C Non competitive atrial pacing
D AF suppression
E Post mode switch overdrive pacing
Question 30
A patient has a dual chamber pacemaker with MRI compatible device and lead set. Prior to their scan, their underlying rhythm is sinus rhythm 75bpm with no ventricular conduction at VVI 30. All other parameters meet criteria for the MRI scan. What is the ideal programming for the scan?
A DOO 90
B DOO 60
C VOO 80
D ODO
Question 31
Which of the following options is it inappropriate to use a magnet over the device?
A When there is pacemaker inhibition during use of diathermy in surgery
B During an MRI scan
C When a pace dependent patient comes in with inappropriate pacing inhibition and syncope
D When a patient is having a PMT
Question 32
What would be the treatment for a patient presenting with infrequent, but severe symptoms of syncope?
A Dual chamber pacemaker
B Single chamber pacemaker
C Implantable loop recorder
D No device indicated
Question 33
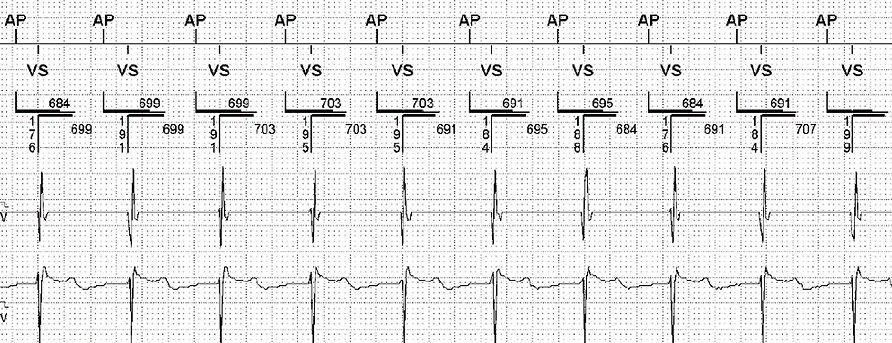
The EGMs in Figure 8 are from a dual chamber device programmed DDI 70, AV 350ms. Which of the following is a potential reason for pacing at this rate?
A Ventricular based timing
B VIP
C Atrial fibrillation suppression pacing
D Rate response
E A and B
F A and C
Figure 8
Question 34
Unnecessary ventricular pacing due to poor programming may result in all of the following except
A Increased risk of arrhythmia
B Reduced left ventricular function
C Atrial and ventricular dysynchrony
D Increased risk in hospitilisation for heart failure
Question 35
An 80 year old patient was implanted with a dual chamber pacemaker for chronotropic incompetence. Based on this information alone, what is the ideal programming for the patient?
A DDD 60-120 with MVP
B DDD 60-120 with normal AV delays
C DDDR 60-120 with MVP
D DDDR 60-120 with normal AV delays
E DDDR 60-120 with rate drop response and MVP
F DDDR 60-120 with rate drop response and normal AV delays
Question 36
All of the following are benefits of auto threshold testing except for
A Tracks a trend of threshold data
B May increase battery longevity
C Can adapt output for rising thresholds
D Can adapt sensing for rising thresholds
Question 37
An 80 year old female has a dual chamber pacemaker with the following settings; DDD 60-130, PAV 180ms, SAV 150ms. A patient is currently in a typical PMT at a rate of 120bpm. The ventriculoatrial conduction time can be determined by which equation?
A 500 – 180
B 500 – 150
C 130 - 60
D none of the above
Question 38
What would the physician do with situation in figure 9 if the pacemaker did not respond to programming. In this example ventricular capture was lost in the bottom strip.
A try another programmer
B detach the pacemaker leads from device
C cardiovert patient
D administer lidocaine
Figure 9

Question 39
Based on the x ray in figure 10, which of the following would we expect to occur
A a low out of range atrial impedance
B a high out of range lead impedance
C a failure to atrial pace detected on the marked channels
D safety pacing or crosstalk
Figure 10

Question 40
Which of the following would most commonly account for a failure to mode switch in the presence of atrial flutter
A atrial blanking
B insufficient atrial sensitivity
C innapropriate atrial sensivity
D varying p wave amplitdes
Question 41
Figure 11 was taken from a patient with sinus bradycardia and normal AV conduction of about 140ms. Following an atrial capture test the patient displayed RNRVAS. Characteristics include which of the following
A retrograde conduction, functional non sensing and functional non capture
B atrial tracking, retrograde conduction and PVC initiation
C antegrade conduction, retrograde conduction and functional oversensing
D retrograde conduction via bypass and functional nonsensing

Figure 11
Question 42
Which of the following features would best explain the ECG in Figure 12
A AAIR with sudden rate acceleration
B DDDR with rate adaptive rate smoothing
C DVIR with rate hysteresis
D DDD with rate drop response

Figure 12
Question 43
Which of the following algorithms may help prevent the early recurrence of AF
A NCAP
B PMOP
C VSP
D NIPS
Question 44
Which of the following would be an example of a closed loop sensor?
A QT interval
B myocardial contractility
C accerlerometer
D piezoelectric crystal
Question 45
A 75 year old male has a dual chamber St Jude Medical Integrity pacemaker that was inserted 8 years ago? The patient comes into clinic for a regular check up. The battery longevity information is as follows; 1.5 years, 5800ohms, 2.75V. When should there next appointment be booked for?
A 12 months
B 9 months
C 6 months
D 3 months
E Book for generator change in the next month
Question 46
Which part of the doctor is considered part of the sterile field?
A neck
B right shoulder
C left hip
D back
Question 47
Extensive ecchymosis that is not expanding following device implantation should be treated by
A observation
B evacuation
C removing oral anticoagulants
D topical application of thrombin
Question 48
Which of the following would be most helpful in diagnosing a lead inadvertently placed in the LV
A an AP x-ray and a RBBB QRS pattern
B a lateral x-ray and a RBBB QRS pattern
C an AP x-ray and a LBBB QRS pattern
D a lateral x-ray and a LBBB QRS pattern
Question 49
Had a back up pulse been delivered at the arrow marked “A” in figure 13, what would you do next?
A turn off autocapture
B program the sensing to unipolar
C replace the ventricular lead
D repeat the evoked response sensitivity test
E A or D
F A, B or D
G A or C
Figure 13

Question 50
Immediately after implant, a patient experiences chest pain and shortness of breath. There is no hypotension, pulsus paradoxus or electrical alternans. What is the most likely explanation?
A cardiac tamponade
B myocardial infarction
C pneumothorax
D anxiety from the procedure





