Heart failure diagnostics
Fluid retention
Mean daily thoracic impedance measurement is made between the can and RV lead and is compared to a reference impedance

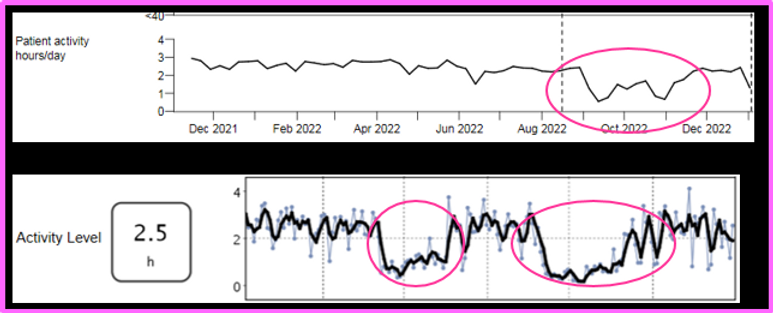
Decline in physical activity
Predictor in mortality and hospitalisation for HF
Decline in heart rate variability (HRV)
Variation in each heart beat (sinus rhythm only)
Measurable reflection of this balance between sympathetic and parasympathetic tone by RR
HRV is depressed in patients with CHF compared with healthy subjects
Among patients with CHF, HRV is further decreased in patients with more advanced NYHA class, lower EF and in those with diabetes, hypertension or VT on Holter monitoring

Decline in heart rate variability (HRV)
Although it is very useful obtaining this diagnostic information off a device, a clinical assessment must be performed (by a physician) to confirm diagnosis
Fluid retention confirmed via the following methods
•Evaluating lung sounds
•Assessing peripheral edema (e.g., swollen ankles)
•Jugular venous distention: bulging neck veins
•Hepatojugular reflux (HJR): distension of the neck veins when pressure is applied to the liver:
-normal heart: JVD then resolves
-HF pts: JVD does not resolve
•Assess presence of extra heart sounds





